PR Interval
PR Interval
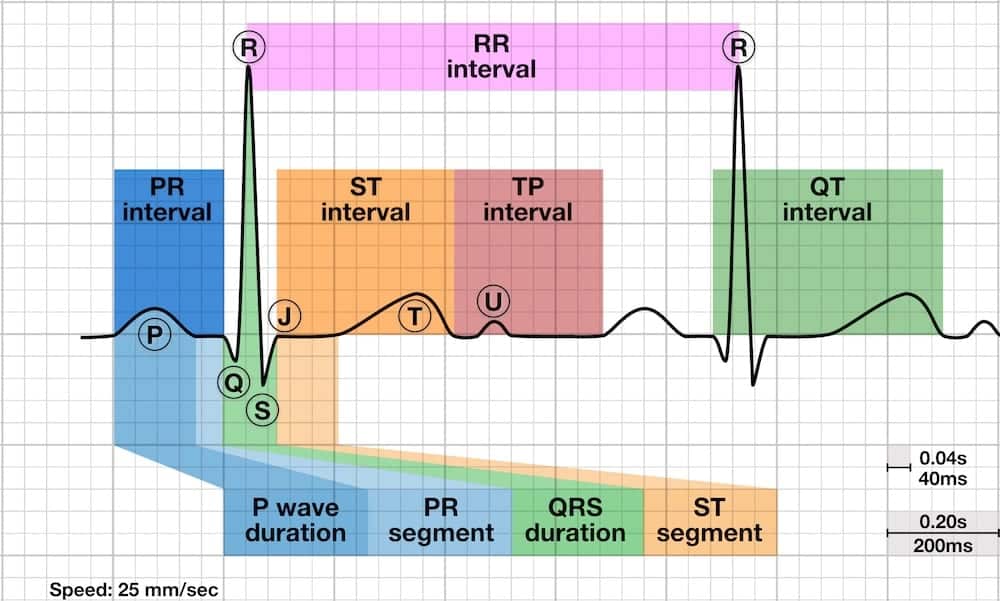
The PR interval is the time from the onset of the P wave to the start of the QRS complex. It reflects conduction through the AV node.
- The normal PR interval is between 120 – 200 ms (0.12-0.20s) in duration (three to five small squares).
- If the PR interval is > 200 ms, first degree heart block is said to be present.
- PR interval < 120 ms suggests pre-excitation (the presence of an accessory pathway between the atria and ventricles) or AV nodal (junctional) rhythm.
Prolonged PR Interval – AV block (PR >200ms)
- Delayed conduction through the AV node
- May occur in isolation or co-exist with other blocks (e.g., second-degree AV block, trifascicular block)
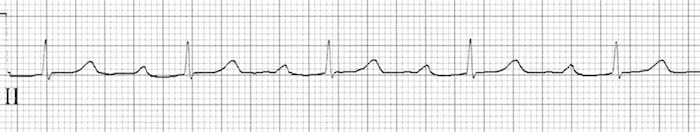
First degree AV block
- Sinus rhythm with marked 1st degree heart block (PR interval 340ms)
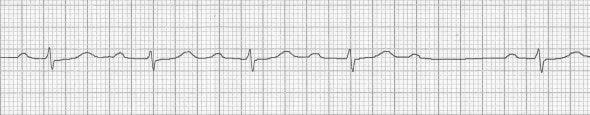
Second degree AV block (Mobitz I) with prolonged PR interval
- Second degree heart block, Mobitz type I (Wenckebach phenomenon).
- Note how the baseline PR interval is prolonged, and then further prolongs with each successive beat, until a QRS complex is dropped.
- The PR interval before the dropped beat is the longest (340ms), while the PR interval after the dropped beat is the shortest (280ms).
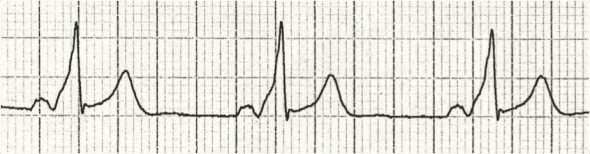
Short PR interval (<120ms)
A short PR interval is seen with:
- Preexcitation syndromes
- AV nodal (junctional) rhythm.
Pre-excitation syndromes
- Wolff-Parkinson-White (WPW) and Lown-Ganong-Levine (LGL) syndromes.
- These involve the presence of an accessory pathway connecting the atria and ventricles.
- The accessory pathway conducts impulses faster than normal, producing a short PR interval.
- The accessory pathway also acts as an anatomical re-entry circuit, making patients susceptible to re-entry tachyarrhythmias.
- Patients present with episodes of paroxsymal supraventricular tachycardia (SVT), specifically atrioventricular re-entry tachycardia (AVRT), and characteristic features on the resting 12-lead ECG.
Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome
The characteristic features of Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome are a short PR interval (<120ms), broad QRS and a slurred upstroke to the QRS complex, the delta wave.
Lown-Ganong-Levine syndrome
The features of Lown-Ganong-Levine syndrome LGL syndrome are a very short PR interval with normal P waves and QRS complexes and absent delta waves.
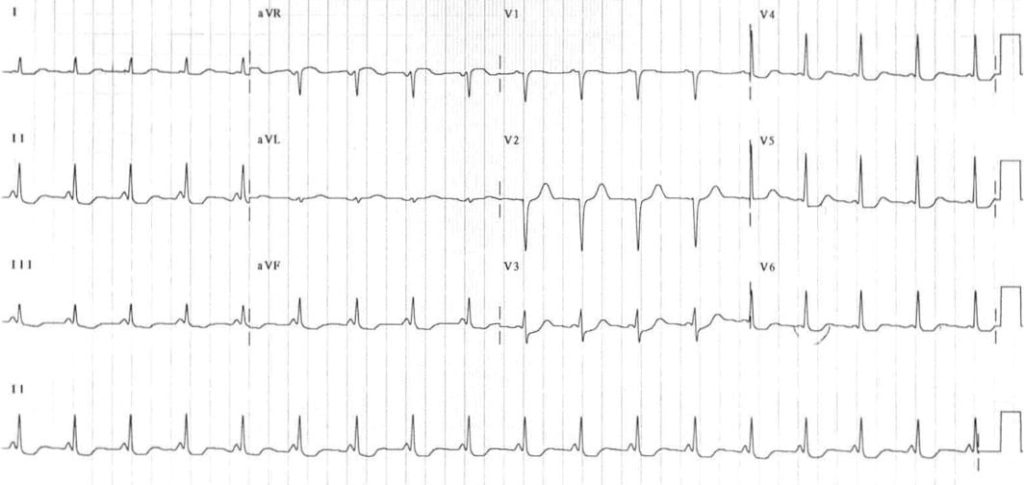
AV nodal (junctional) rhythm
- Junctional rhythms are narrow complex, regular rhythms arising from the AV node.
- P waves are either absent or abnormal (e.g. inverted) with a short PR interval (=retrograde P waves).
- ECG: Accelerated junctional rhythm demonstrating inverted P waves with a short PR interval (retrograde P waves)
ECG Library Basics
Advanced Reading
Online
- Wiesbauer F, Kühn P. ECG Mastery: Yellow Belt online course. Understand ECG basics. Medmastery
- Wiesbauer F, Kühn P. ECG Mastery: Blue Belt online course: Become an ECG expert. Medmastery
- Kühn P, Houghton A. ECG Mastery: Black Belt Workshop. Advanced ECG interpretation. Medmastery
- Rawshani A. Clinical ECG Interpretation ECG Waves
- Smith SW. Dr Smith’s ECG blog.
- Wiesbauer F. Little Black Book of ECG Secrets. Medmastery PDF
Textbooks
- Zimmerman FH. ECG Core Curriculum. 2023
- Mattu A, Berberian J, Brady WJ. Emergency ECGs: Case-Based Review and Interpretations, 2022
- Straus DG, Schocken DD. Marriott’s Practical Electrocardiography 13e, 2021
- Brady WJ, Lipinski MJ et al. Electrocardiogram in Clinical Medicine. 1e, 2020
- Mattu A, Tabas JA, Brady WJ. Electrocardiography in Emergency, Acute, and Critical Care. 2e, 2019
- Hampton J, Adlam D. The ECG Made Practical 7e, 2019
- Kühn P, Lang C, Wiesbauer F. ECG Mastery: The Simplest Way to Learn the ECG. 2015
- Grauer K. ECG Pocket Brain (Expanded) 6e, 2014
- Surawicz B, Knilans T. Chou’s Electrocardiography in Clinical Practice: Adult and Pediatric 6e, 2008
- Chan TC. ECG in Emergency Medicine and Acute Care 1e, 2004
LITFL Further Reading
- ECG Library Basics – Waves, Intervals, Segments and Clinical Interpretation
- ECG A to Z by diagnosis – ECG interpretation in clinical context
- ECG Exigency and Cardiovascular Curveball – ECG Clinical Cases
- 100 ECG Quiz – Self-assessment tool for examination practice
- ECG Reference SITES and BOOKS – the best of the rest
ECG LIBRARY