Multifocal Atrial Tachycardia (MAT)
Multifocal Atrial Tachycardia (MAT) Overview
- A rapid, irregular atrial rhythm arising from multiple ectopic foci within the atria.
- Most commonly seen in patients with severe COPD or congestive heart failure.
- It is typically a transitional rhythm between frequent premature atrial complexes (PACs) and atrial flutter / fibrillation.
AKA “Chaotic atrial tachycardia”
Electrocardiographic Features
- Heart rate > 100 bpm (usually 100-150 bpm; may be as high as 250 bpm).
- Irregularly irregular rhythm with varying PP, PR and RR intervals.
- At least 3 distinct P-wave morphologies in the same lead.
- Isoelectric baseline between P-waves (i.e. no flutter waves).
- Absence of a single dominant atrial pacemaker (i.e. not just sinus rhythm with frequent PACs).
- Some P waves may be nonconducted; others may be aberrantly conducted to the ventricles.
There may be additional electrocardiographic features suggestive of COPD.
Clinical Relevance
- Usually occurs in seriously ill elderly patients with respiratory failure (e.g. exacerbation of COPD / CHF).
- Tends to resolve following treatment of the underlying disorder.
- The development of MAT during an acute illness is a poor prognostic sign, associated with a 60% in-hospital mortality and mean survival of just over a year. Death occurs due to the underlying illness; not the arrhythmia itself.
Mechanism
Arises due to a combination of factors that are present in hospitalised patients with acute-on-chronic respiratory failure:
- Right atrial dilatation (from cor pulmonale)
- Increased sympathetic drive
- Hypoxia and hypercarbia
- Beta-agonists
- Theophylline
- Electrolyte abnormalities: Hypokalaemia and hypomagnesaemia (e.g. secondary to diuretics / beta-agonists)
The net result is increased atrial automaticity.
ECG Examples
Example 1
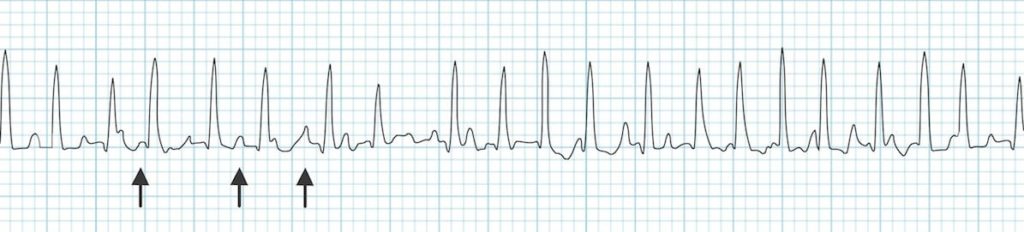
Multifocal atrial tachycardia:
- Rapid irregular rhythm > 100 bpm.
- At least 3 distinctive P-wave morphologies (arrows).
Example 2
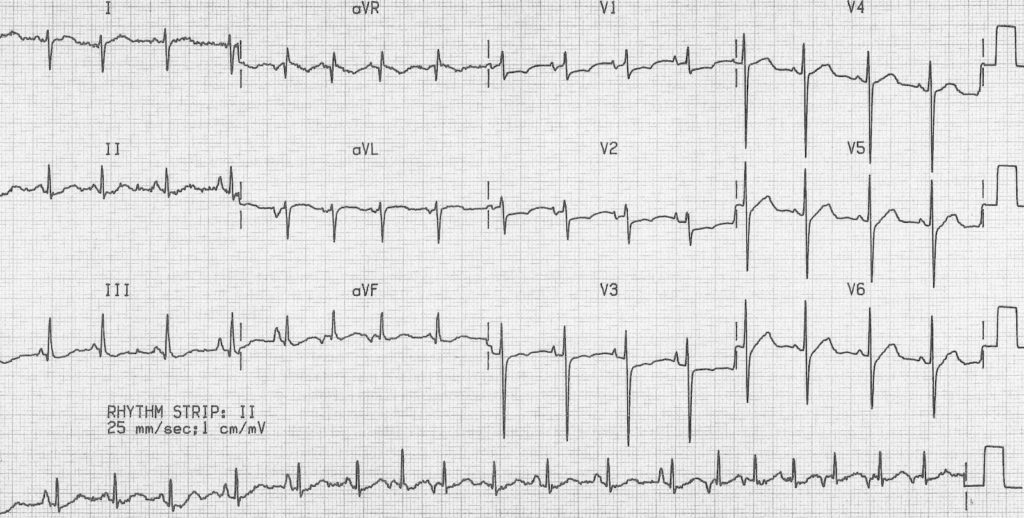
MAT with additional features of COPD:
- Rapid, irregular rhythm with multiple P-wave morphologies (best seen in the rhythm strip).
- Right axis deviation, dominant R wave in V1 and deep S wave in V6 suggest right ventricular hypertrophy due to cor pulmonale.
Related Topics
Advanced Reading
Online
- Wiesbauer F, Kühn P. ECG Mastery: Yellow Belt online course. Understand ECG basics. Medmastery
- Wiesbauer F, Kühn P. ECG Mastery: Blue Belt online course: Become an ECG expert. Medmastery
- Kühn P, Houghton A. ECG Mastery: Black Belt Workshop. Advanced ECG interpretation. Medmastery
- Rawshani A. Clinical ECG Interpretation ECG Waves
- Smith SW. Dr Smith’s ECG blog.
- Wiesbauer F. Little Black Book of ECG Secrets. Medmastery PDF
Textbooks
- Zimmerman FH. ECG Core Curriculum. 2023
- Mattu A, Berberian J, Brady WJ. Emergency ECGs: Case-Based Review and Interpretations, 2022
- Straus DG, Schocken DD. Marriott’s Practical Electrocardiography 13e, 2021
- Brady WJ, Lipinski MJ et al. Electrocardiogram in Clinical Medicine. 1e, 2020
- Mattu A, Tabas JA, Brady WJ. Electrocardiography in Emergency, Acute, and Critical Care. 2e, 2019
- Hampton J, Adlam D. The ECG Made Practical 7e, 2019
- Kühn P, Lang C, Wiesbauer F. ECG Mastery: The Simplest Way to Learn the ECG. 2015
- Grauer K. ECG Pocket Brain (Expanded) 6e, 2014
- Surawicz B, Knilans T. Chou’s Electrocardiography in Clinical Practice: Adult and Pediatric 6e, 2008
- Chan TC. ECG in Emergency Medicine and Acute Care 1e, 2004
LITFL Further Reading
- ECG Library Basics – Waves, Intervals, Segments and Clinical Interpretation
- ECG A to Z by diagnosis – ECG interpretation in clinical context
- ECG Exigency and Cardiovascular Curveball – ECG Clinical Cases
- 100 ECG Quiz – Self-assessment tool for examination practice
- ECG Reference SITES and BOOKS – the best of the rest
ECG LIBRARY
Emergency Physician in Prehospital and Retrieval Medicine in Sydney, Australia. He has a passion for ECG interpretation and medical education | ECG Library |
MBBS DDU (Emergency) CCPU. Adult/Paediatric Emergency Medicine Advanced Trainee in Melbourne, Australia. Special interests in diagnostic and procedural ultrasound, medical education, and ECG interpretation. Co-creator of the LITFL ECG Library. Twitter: @rob_buttner

