Normal paediatric ECG
ECG Features
The following electrocardiographic features may be normal in children:
- Heart rate > 100 beats/min
- Apparent right ventricular strain pattern:
- T wave inversions in V1-3 (“juvenile T-wave pattern”)
- Right axis deviation
- Dominant R wave in V1
- RSR’ pattern in V1
- Marked sinus arrhythmia
- Short PR interval (< 120ms) and QRS duration (<80ms)
- Slightly peaked P waves (< 3mm in height is normal if ≤ 6 months)
- Slightly prolonged QTc (≤ 490ms in infants ≤ 6 months)
- Q waves in the inferior and left precordial leads
Pathophysiology
At birth, the right ventricle is larger and thicker than the left ventricle, reflecting greater physiological stresses placed upon it in utero (i.e. pumping blood through the relatively high-resistance pulmonary circulation).
This produces an ECG picture reflecting that of a right ventricular strain pattern in adults:
- T-wave inversions in V1-3
- Right axis deviation
- Dominant R wave in V1
Conduction intervals (PR interval, QRS duration) are shorter than adults due to the smaller cardiac size.
Heart rates are highest in neonates and infants and decrease with age:
- Newborn: 110 – 150 bpm
- 2 years: 85 – 125 bpm
- 4 years: 75 – 115 bpm
- > 6 years: 60 – 100 bpm
The right ventricular dominance of the neonate and infant is gradually replaced by left ventricular dominance so that by 3-4 years of age, the paediatric ECG largely resembles that of adults.
ECG Examples
Example 1
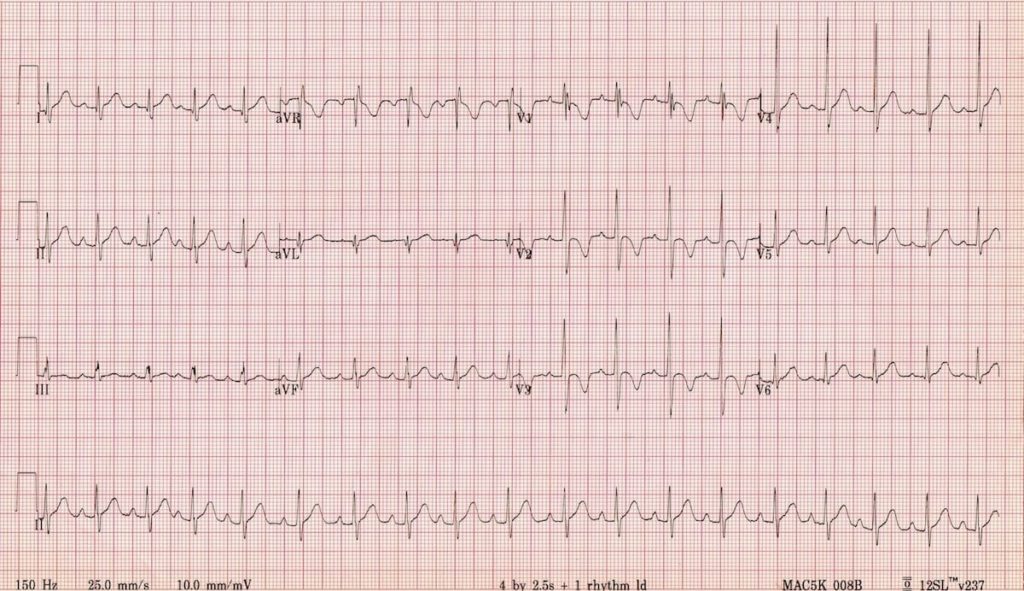
This ECG of a healthy 2-year old boy displays many of the typical features of the paediatric ECG:
- Heart rate of 110 bpm (normal for age)
- Juvenile T-wave pattern (T wave inversion in V1-3)
- Dominant R waves in V1-3
- RSR’ pattern (partial RBBB morphology) in V1
Further normal ECG examples
Normal ECG : 1 Year
- Sinus rhythm ~150 beats/min
- Right axis deviation
- T wave inversion in V1-3
- Dominant R wave in V1
- Narrow QRS complex
Normal ECG : 2 Years
- Similiar findings to above, now with borderline right axis deviation and an upright T wave in V3
Normal ECG : 5 Years
- Rate has slowed, axis is normal, and QRS width has begun to normalise
- Persisting T wave inversion in V2
Normal ECG : 10 Years
Related Topics
- Paediatric ECG Basics
- Paediatric lead placement
- Stepwise assessment of the paediatric ECG
- Common paediatric arrhythmias
- ECG approach in syncope
References
- Paediatric Electrocardiography by Steve Goodacre and Karen McLeod, from the BMJ’s “ABC of Clinical Electrocardiography” series (2002)
- O’Connor M, McDaniel N, Brady WJ. The pediatric electrocardiogram. Part I: Age-related interpretation. Am J Emerg Med. 2008 Feb;26(2):221-8
- Evans WN1, Acherman RJ, Mayman GA, Rollins RC, Kip KT. Simplified pediatric electrocardiogram interpretation. Clin Pediatr (Phila). 2010 Apr;49(4):363-72.
Advanced Reading
Online
- Wiesbauer F, Kühn P. ECG Mastery: Yellow Belt online course. Understand ECG basics. Medmastery
- Wiesbauer F, Kühn P. ECG Mastery: Blue Belt online course: Become an ECG expert. Medmastery
- Kühn P, Houghton A. ECG Mastery: Black Belt Workshop. Advanced ECG interpretation. Medmastery
- Rawshani A. Clinical ECG Interpretation ECG Waves
- Smith SW. Dr Smith’s ECG blog.
- Wiesbauer F. Little Black Book of ECG Secrets. Medmastery PDF
Textbooks
- Zimmerman FH. ECG Core Curriculum. 2023
- Mattu A, Berberian J, Brady WJ. Emergency ECGs: Case-Based Review and Interpretations, 2022
- Straus DG, Schocken DD. Marriott’s Practical Electrocardiography 13e, 2021
- Brady WJ, Lipinski MJ et al. Electrocardiogram in Clinical Medicine. 1e, 2020
- Mattu A, Tabas JA, Brady WJ. Electrocardiography in Emergency, Acute, and Critical Care. 2e, 2019
- Hampton J, Adlam D. The ECG Made Practical 7e, 2019
- Kühn P, Lang C, Wiesbauer F. ECG Mastery: The Simplest Way to Learn the ECG. 2015
- Grauer K. ECG Pocket Brain (Expanded) 6e, 2014
- Surawicz B, Knilans T. Chou’s Electrocardiography in Clinical Practice: Adult and Pediatric 6e, 2008
- Chan TC. ECG in Emergency Medicine and Acute Care 1e, 2004
LITFL Further Reading
- ECG Library Basics – Waves, Intervals, Segments and Clinical Interpretation
- ECG A to Z by diagnosis – ECG interpretation in clinical context
- ECG Exigency and Cardiovascular Curveball – ECG Clinical Cases
- 100 ECG Quiz – Self-assessment tool for examination practice
- ECG Reference SITES and BOOKS – the best of the rest
ECG LIBRARY
Emergency Physician in Prehospital and Retrieval Medicine in Sydney, Australia. He has a passion for ECG interpretation and medical education | ECG Library |
MBBS DDU (Emergency) CCPU. Adult/Paediatric Emergency Medicine Advanced Trainee in Melbourne, Australia. Special interests in diagnostic and procedural ultrasound, medical education, and ECG interpretation. Co-creator of the LITFL ECG Library. Twitter: @rob_buttner

