
Mark Ravitch
Mark M. Ravitch, pioneering pediatric surgeon, innovator of the Ravitch procedure, stapling, intussusception care, and Cantrell’s sequence.

Mark M. Ravitch, pioneering pediatric surgeon, innovator of the Ravitch procedure, stapling, intussusception care, and Cantrell’s sequence.

William John Adie (1886 – 1935) was an Australian neurologist. Best known for describing the tonically dilated pupil (Adie pupil) associated with absent deep tendon reflexes (Adie syndrome) and his description of narcolepsy

Irish neurologist Sir Gordon Holmes (1876–1965), pioneer of cerebellar and visual pathway research, key wartime studies, and enduring neurological eponym

German physician Bernhard Naunyn (1839–1925), pioneer of experimental medicine, defined acidosis, advanced diabetes and gallstone research, and co-founded Naunyn–Schmiedeberg’s Archives

German physician Heinrich Quincke (1842–1922) pioneered lumbar puncture and described Quincke’s pulse, oedema, triad, and more thus shaping modern clinical medicine

Hans Kehr (1862–1916), pioneer of gallbladder surgery, introduced the T-tube for bile duct drainage; eponymously linked to Kehr’s sign of splenic rupture.

Stephen Stigler, statistician and historian, coined Stigler’s Law of Eponymy and advanced the history of statistics through influential books and research
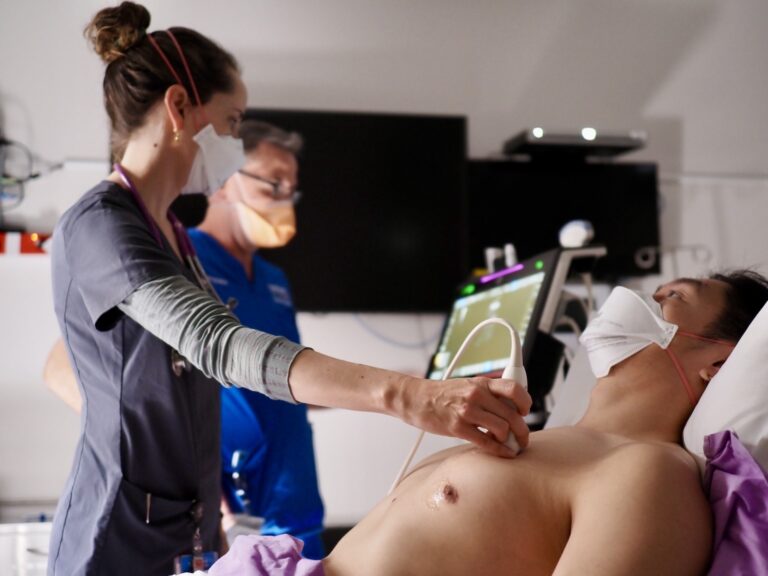
Everyone loves knob twiddling on machines that go ping! But how do you knobologise a touchscreen? Get ready to finger your way into POCUS.

Scottish surgeon Sir William Macewen (1848–1924) pioneered neurosurgery, bone grafting, and antiseptic technique, transforming modern surgical practice

Emergency Procedure, instruction and discussion: Serratus Anterior Plane (SAP) Block; a technique most often used for rib fracture pain
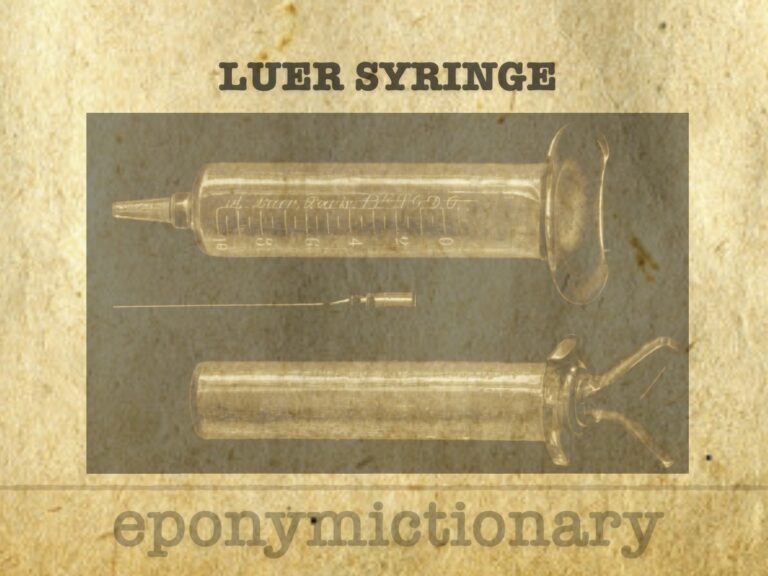
Lüer syringe (1894). Unique graduated all-glass hypodermic syringe. Invented by Jeanne Amélie Lüer; Patented by Wülfing-Lüer
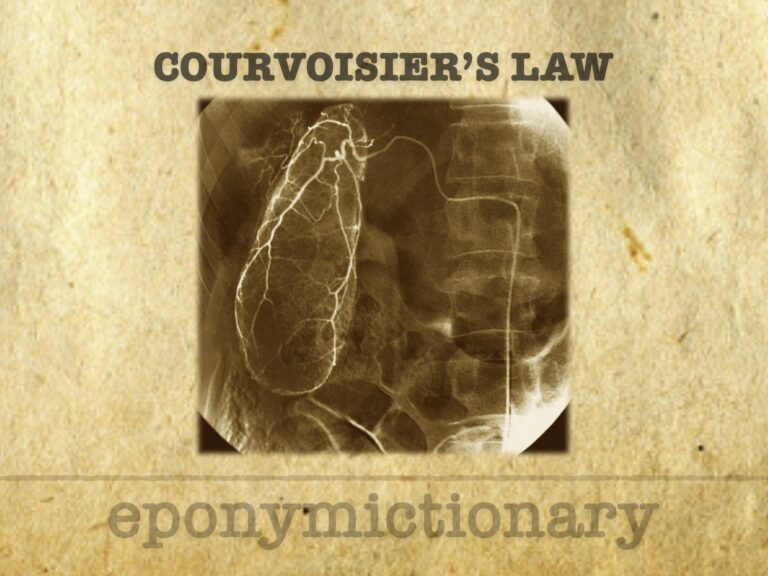
Courvoisier’s sign: palpable gallbladder with painless jaundice suggests malignant obstruction, not gallstones. A key clinical diagnostic clue.