Libman-Sacks endocarditis
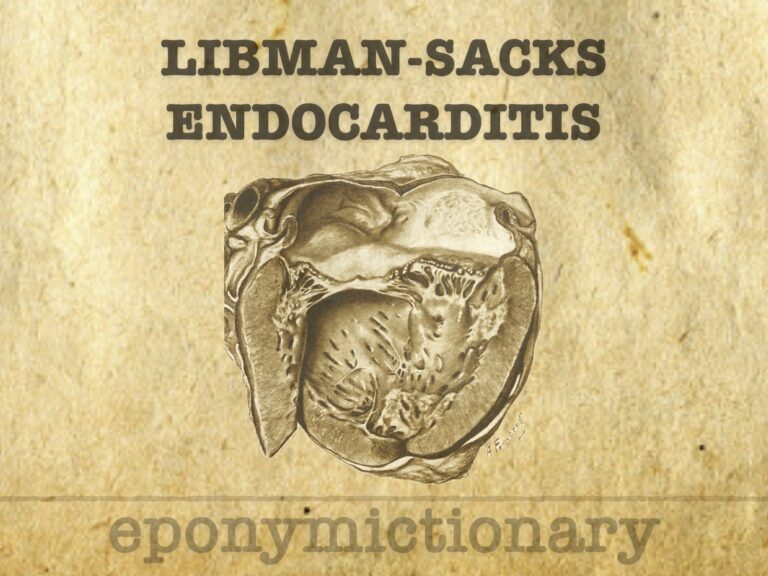
Libman–Sacks endocarditis is a sterile cardiac valve lesion linked to lupus and antiphospholipid syndrome, often detected via echocardiography

Libman–Sacks endocarditis is a sterile cardiac valve lesion linked to lupus and antiphospholipid syndrome, often detected via echocardiography

Emanuel Libman (1872–1946), American internist who co-described Libman-Sacks endocarditis and revolutionised diagnostic medicine at Mount Sinai.

Benjamin Sacks (1896–1971), cardiac pathologist and co-describer of Libman–Sacks endocarditis, also a Hollywood advisor and Arizona frontier historian.

Sidney Yankauer (1872–1932), American ENT surgeon and inventor of the Yankauer suction catheter, pioneer in bronchoscopy and surgical airway care

Adolphe-Marie Gubler (1821-1879) was a French physician and therapeutic pharmacologist. Millard-Gubler syndrome (1856)

Auguste Louis Jules Millard (1830-1915) was a French physician. Millard-Gubler syndrome (1856). Master educator and physician
Common viral illness in infants caused by HHV-6. Roseola presents with high fever followed by sudden rash; also known as sixth disease or exanthem subitum.
Erythema infectiosum (fifth disease), is a common manifestation of infection in children characterized by low-grade fever, malaise, facial rash, and later by the spread of a lacy maculopapular rash involving the trunk and limbs.
Filatov-Dukes disease, or fourth disease, was a proposed childhood exanthem now largely dismissed as a misclassification of rubella or scarlet fever.
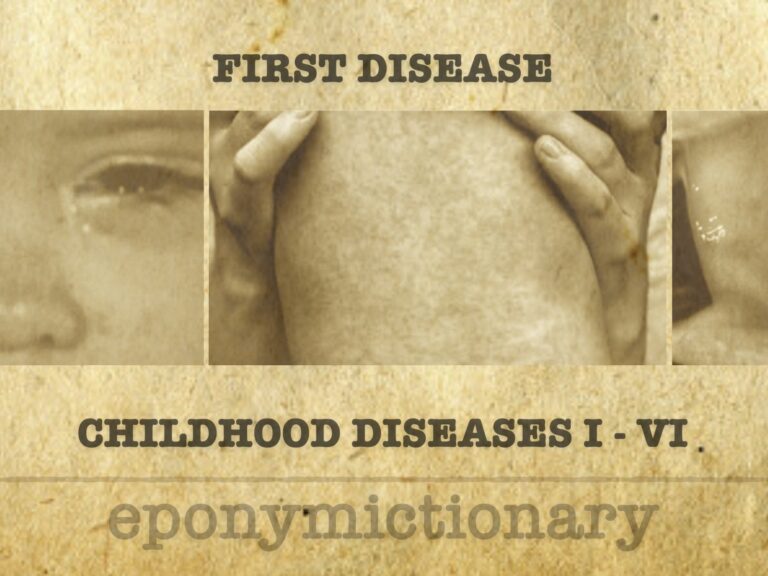
Mild viral exanthem in children; dangerous in pregnancy. Rubella causes rash and lymphadenopathy, with congenital infection leading to CRS.
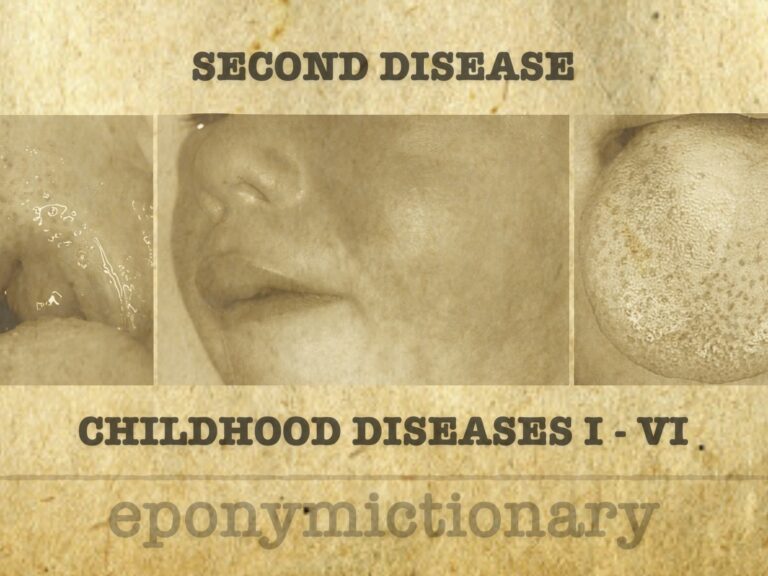
Scarlet fever (second disease). Contagious GABHS infection in kids under 10 with sore throat or rash; caused by S. pyogenes strains producing erythrogenic toxin.
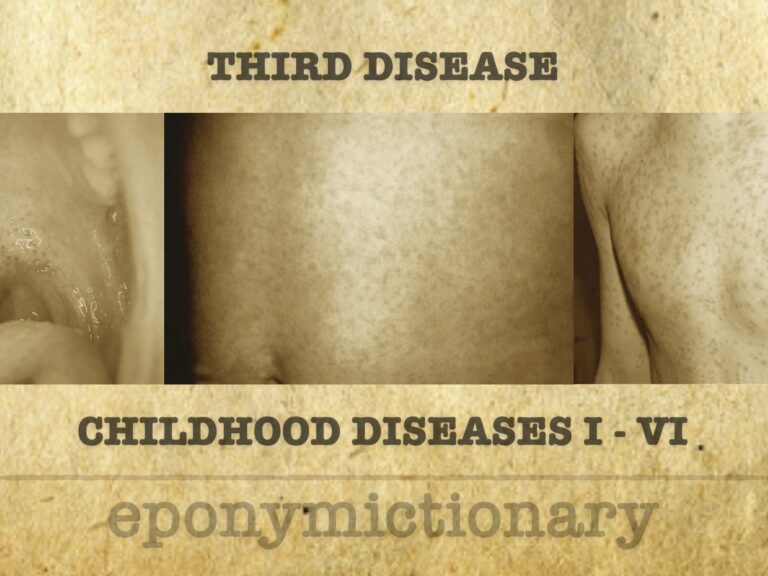
Measles (First Disease): classic childhood exanthem caused by Morbillivirus, with high infectivity, pathognomonic signs, and vaccine-preventable