
Ramsay Hunt Syndrome
Ramsay Hunt Syndrome: clinical features, differential diagnosis from Bell’s palsy, investigations, management with antivirals and steroids, prognosis.

Ramsay Hunt Syndrome: clinical features, differential diagnosis from Bell’s palsy, investigations, management with antivirals and steroids, prognosis.

Margaret Dix (1911–1991), British neuro-otologist who co-developed the Dix–Hallpike test, reshaped diagnosis of vertigo and advanced vestibular science

Overview of Bell’s palsy: causes, clinical features, complications, diagnosis, differential diagnoses, investigations, and management including steroids, eye care, and antivirals

A 54-year-old lady with end stage renal failure (ERSF) presents to the the emergency department with abdominal pain.

Limb ischaemia is generally classified on the basis of its onset and severity, and may be complete, incomplete or irreversible

Emergency procedure, instructions and discussion: Postpartum haemorrhage (PPH). Take a few deep breaths and your own pulse, then dive into the video

Harold Leeming Sheehan (1900-1988) was an English physician and pathologist. Eponymously remembered for his description of Sheehan Syndrome in 1937
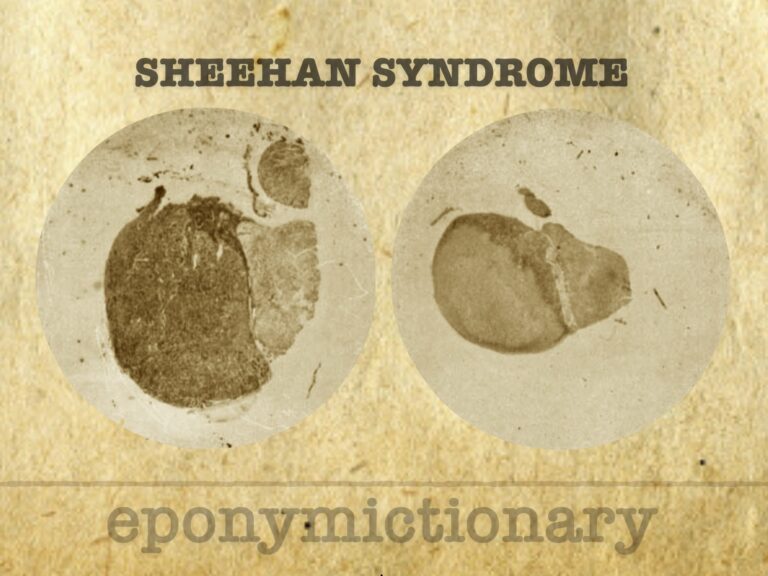
Postpartum hypopituitarism following ischaemic necrosis of the anterior pituitary gland. Pituitary necrosis occurs secondary to hypophyseal portal vessel thrombosis following significant postpartum haemorrhage, hypovolemia, and shock.

Overview of Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm: presentation, risk factors, rupture risk, clinical features, investigations, emergency management, and surgical options

Critical Care Compendium pharmacology entry for prazosin.

Swiss physician Gaspard Vieusseux (1746–1814) described cerebrospinal meningitis in 1805 and gave the first clinical account of lateral medullary syndrome.

Lemierre syndrome is infective thrombophlebitis of the internal jugular vein caused primarily by anaerobic organisms from a focus of oropharyngeal infection