
Abraham Jacobi
German-born American pediatrician Abraham Jacobi (1830–1919) founded U.S. pediatrics, led reform in child health, and shaped medical education and policy.

German-born American pediatrician Abraham Jacobi (1830–1919) founded U.S. pediatrics, led reform in child health, and shaped medical education and policy.

Neuro 101: The brainstem is organised into three regions: the medulla, pons, and midbrain. A review of pathology and syndromes

Pioneer of clinical cardiac electrophysiology, Sir Thomas Lewis (1881–1945) advanced ECG use, defined effort syndrome, and discovered the Lewis Triple Response.
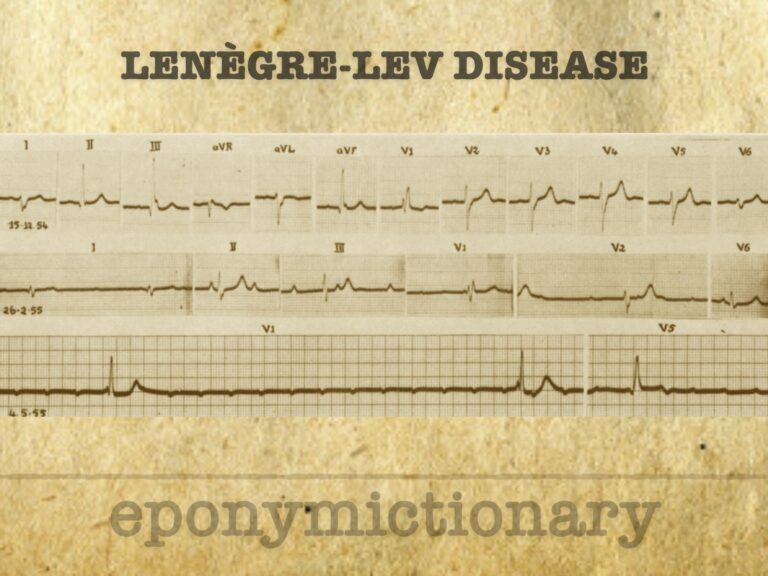
Acquired fibrous degeneration of the left and right bundle branches, eventually manifesting as permanent complete atrioventricular (AV) dissociation with cardiac pauses and Adams-Stokes attacks

Charles Heber McBurney (1845 – 1913) was an American surgeon. Most famous for McBurney's point (1889) and McBurney's incision (1894) Medical Eponym.

The mitral valve is a dominant structure in most standard echocardiographic views. Understanding its anatomy in each window is essential for accurate assessment.

Neuro 101: The primary role of the cerebellum is to modulate the descending fibres of the corticospinal tract. It regulates muscle tone and coordination and controls posture and gait.

Jean Lenègre (1904–1972), French cardiologist, defined Lenègre’s disease and pioneered cardiac electrophysiology, catheterization, and bundle branch pathology

Maurice Lev (1908–1994), pathologist and teacher, defined Lev’s disease and advanced cardiac conduction and congenital heart pathology through over 500 publications

Stokes-Adams syndrome is an abrupt, transient loss of consciousness due to a sudden but pronounced decrease in the cardiac output
Robert Adams (1791–1875), Dublin physician, first described Adams–Stokes syndrome and pioneered clinical-pathological correlation in heart disease

John Cheyne (1777–1836), Irish physician, co-described Cheyne-Stokes respiration, advanced clinical neurology, and linked pupils to brain injury