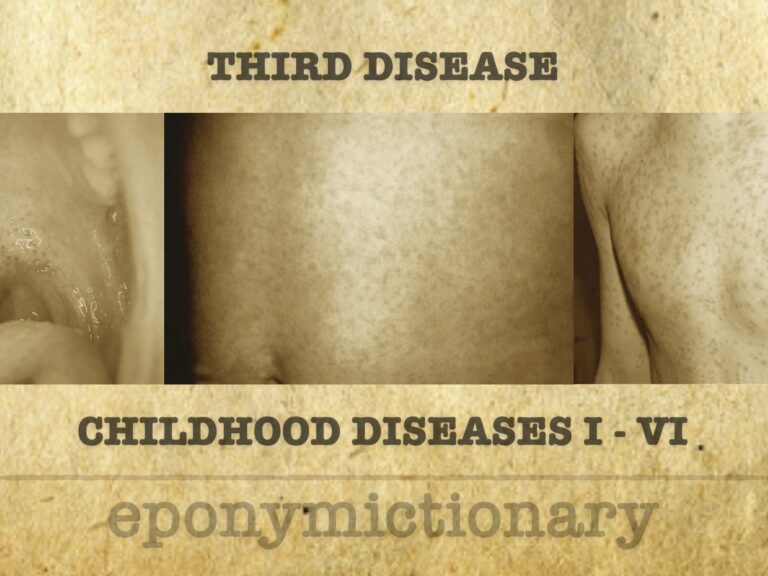
Third disease
Mild viral exanthem in children; dangerous in pregnancy. Rubella causes rash and lymphadenopathy, with congenital infection leading to CRS.

Mild viral exanthem in children; dangerous in pregnancy. Rubella causes rash and lymphadenopathy, with congenital infection leading to CRS.
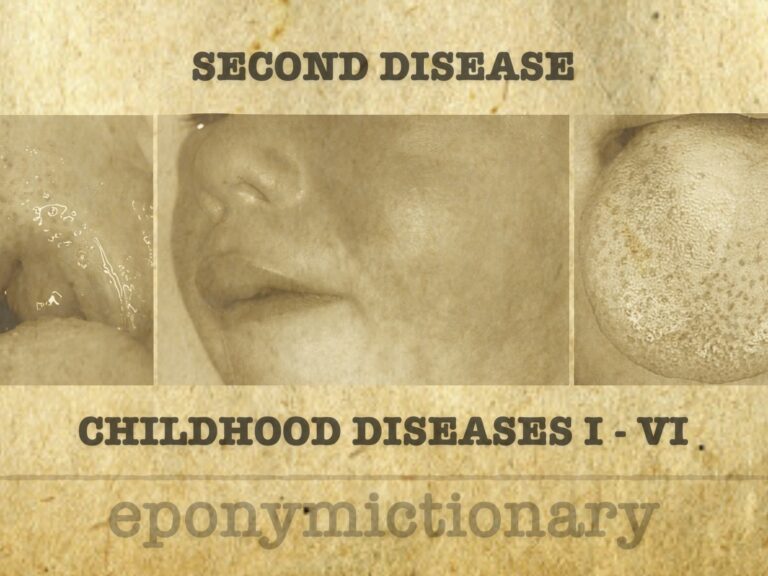
Scarlet fever (second disease). Contagious GABHS infection in kids under 10 with sore throat or rash; caused by S. pyogenes strains producing erythrogenic toxin.
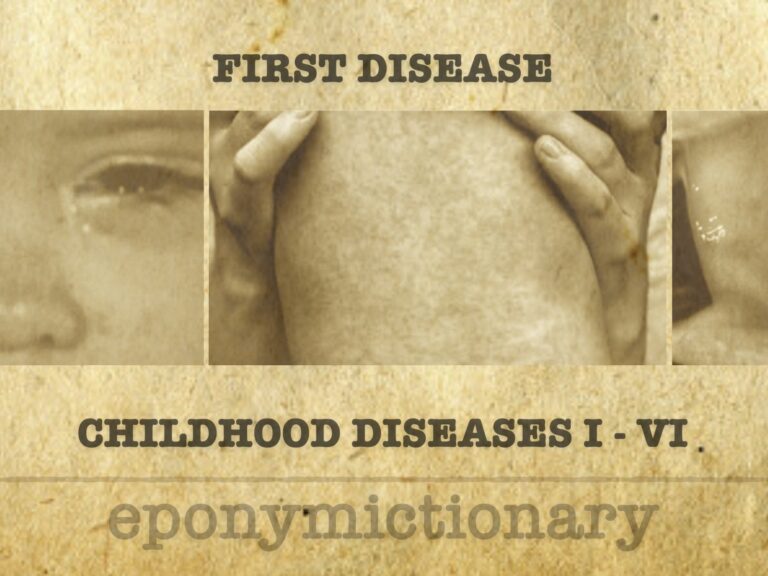
Measles (First Disease): classic childhood exanthem caused by Morbillivirus, with high infectivity, pathognomonic signs, and vaccine-preventable
Clement Dukes (1845–1925), English physician and school health reformer, proposed "Dukes' disease" and transformed adolescent medical care in public schools.
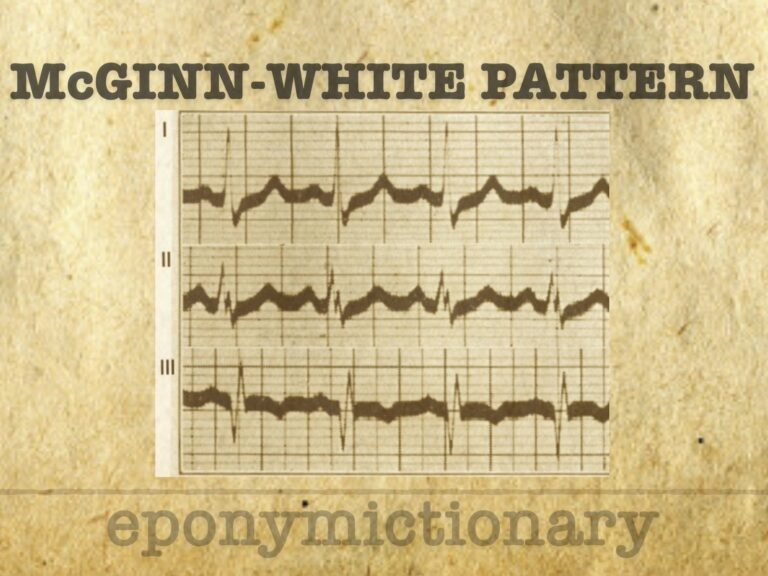
S1Q3T3 McGinn-White pattern indicates right heart strain and predicts severe PE outcomes. ECG sign of pulmonary embolism described in 1935.

Thomas Stephen Cullen (1869 – 1953) was a Canadian gynecologist. Eponymously affiliated with Cullen sign (1918)

George Quentin Chance was an British radiologist. Eponymously associated with the Chance fracture (1948) transverse fracture through a vertebral body

Yvonne Edna Cossart (1934-2014) was an Australian virologist. In 1975, Cossart and her colleagues recognised parvovirus B19

James Ramsay Hunt (1874-1937) American neurologist. Renowned for his contributions to the field of neurology. Several conditions bear his name including Ramsay Hunt syndrome (1907)

Howard Henry Tooth (1856–1925), English neurologist; Charcot–Marie–Tooth disease; specialist in spinal degeneration and wartime medical service.

Eugen von Bamberger (1858–1921), Austrian internist; co-described Marie–Bamberger syndrome (hypertrophic pulmonary osteoarthropathy); pioneer of clinical diagnostics.
Robert Bentley Todd (1809-1860) was an Irish physician. Provided early depictions of migraine, peripheral neuritis, and postepileptic paralysis (Todd's palsy). He also gave an important discourse on locomotor ataxy (tabes dorsalis).