
Left Anterior Fascicular Block (LAFB)
In left anterior fascicular block (LAFB), impulses are conducted to the left ventricle via the posterior fascicle, producing characteristic ECG changes

In left anterior fascicular block (LAFB), impulses are conducted to the left ventricle via the posterior fascicle, producing characteristic ECG changes

Left posterior fascicular block LPFB (left posterior hemiblock), impulses are conducted to the left ventricle via the left anterior fascicle

A review of the ECG features of right ventricular outflow tract tachycardia (RVOT), a type of VT, with example ECGs.

Isolated low serum Mg levels are associated with atrial depolarisation and ventricular repolarisation abnormalities, predisposing to ventricular arrhythmias

Aslanger et al identified a specific ECG pattern concerning for acute inferior occlusion MI in patients with concomitant multi-vessel disease, that does not display contiguous ST-segment elevation or fulfil STEMI criteria

Trifascicular block (TFB) refers to the presence of conducting disease in all three fascicles: RBBB, LAFB, LPFB. LITFL ECG Library

Left Bundle Branch Block LBBB - normal direction of septal depolarisation is reversed (becomes right to left), as the impulse spreads
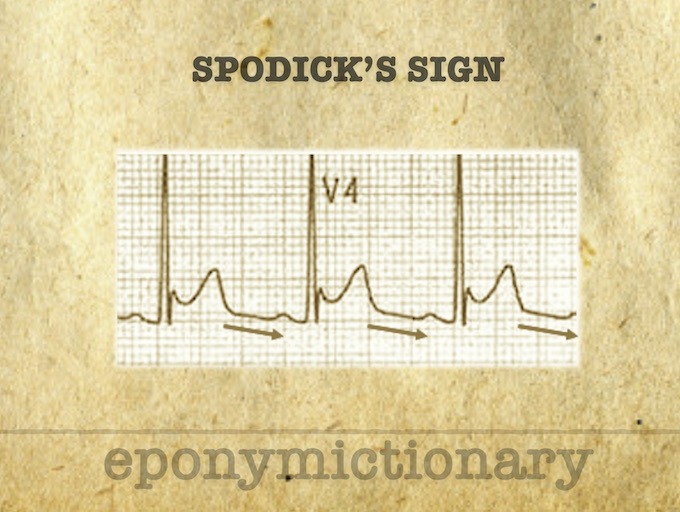
Spodick Sign: Stage I Pericarditis, a downsloping of the TP line. Described 1974 by American Cardiologist, David H Spodick (1927 – 2019)

Right Bundle Branch Block (RBBB) activation of the right ventricle is delayed as depolarisation spreads across septum from left ventricle.

Also known as primary sinus tachycardia, inappropriate sinus tachycardia (IST) is a generally benign condition that has a prevalence of ~1% in the general population

Bifascicular block is the combination of RBBB with either LAFB or LPFB. Conduction to the ventricles is via the single remaining fascicle.

Defined as PR interval > 200ms, commonly caused by AV nodal blocking drugs