Focal Atrial Tachycardia (FAT)
Definition
Focal atrial tachycardia (FAT) is a form of supraventricular tachycardia (SVT) originating from a single ectopic focus within the atria but outside of the sinus node
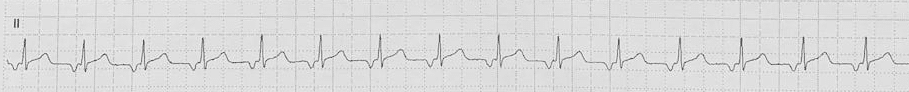
- The term FAT is commonly used synonymously with atrial tachycardia, a broader term referring to any form of SVT originating within the atria but outside of the sinus node
- FAT, atrial flutter and multifocal atrial tachycardia (MAT) are all forms of atrial tachycardia
- Management of the three types varies and thus distinguishing between them is clinically important
Pathophysiology of FAT
- Due to a single ectopic focus
- The underlying mechanism can involve increased automaticity, triggered activity or reentry
- May be paroxysmal or sustained
- Multiple causes including:
- Digoxin toxicity
- Atrial scarring due to ischaemic heart disease
- Catecholamine excess
- Stimulants including cocaine, caffeine
- Alcohol
- Congenital abnormalities
- Idiopathic
- Sustained atrial tachycardia may rarely be seen and can progress to tachycardia-induced cardiomyopathy
ECG Features of Atrial Tachycardia
- Atrial rate > 100 bpm
- Abnormal P wave morphology and axis (e.g. inverted in inferior leads) due to ectopic origin
- Unifocal, identical P waves
- Isoelectric baseline (unlike atrial flutter)
- Normal QRS morphology (unless pre-existing bundle branch block, accessory pathway, or rate-related aberrant conduction)
AV block may be present — this is generally a physiological response to the rapid atrial rate, except in digoxin toxicity where there is AV nodal suppression due to vagotonic effects of digoxin, resulting in a slow ventricular rate (“PAT with block”).
ECG Examples
Example 1
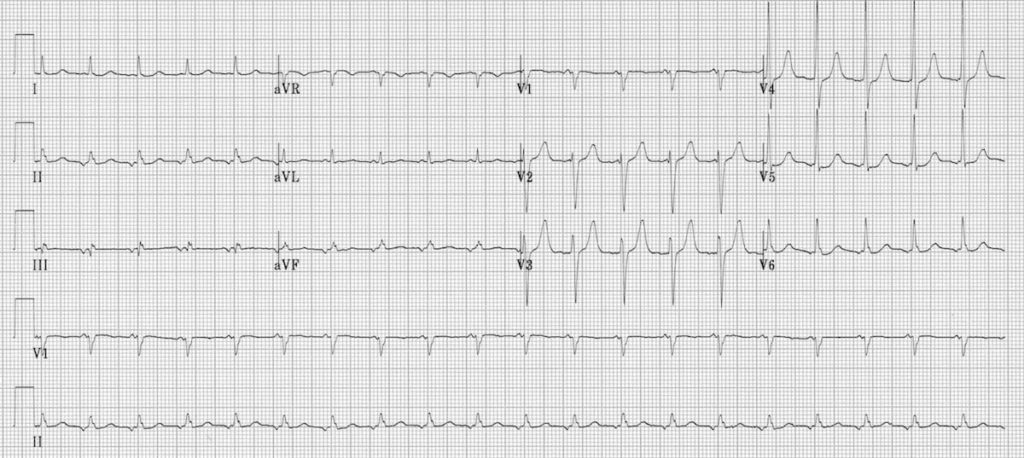
Focal atrial tachycardia:
- There is a narrow complex tachycardia at 120 bpm
- Each QRS complex is preceded by an abnormal P wave — upright in V1, inverted in the inferior leads II, III and aVF
- P wave morphology is consistent throughout
Example 2
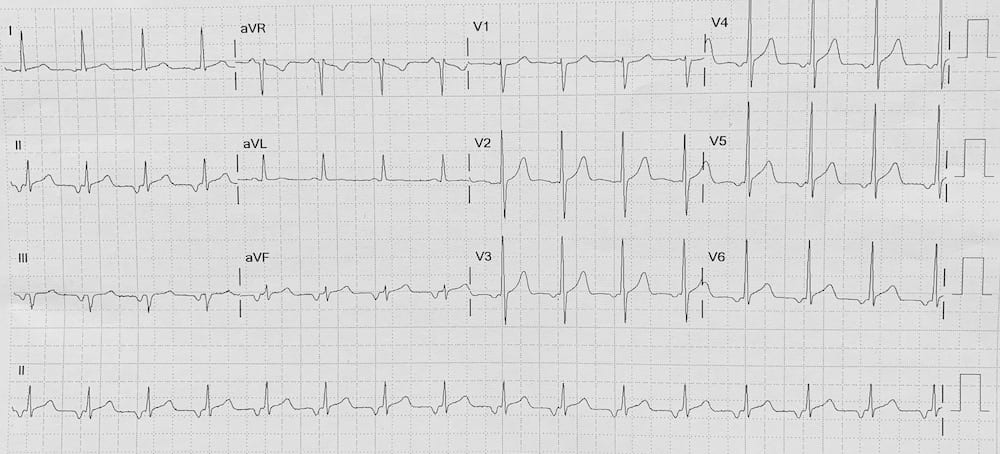
Focal atrial tachycardia:
- There is a narrow complex tachycardia at 95 bpm
- Each QRS complex is preceded by an abnormal P wave — biphasic in V1; inverted in the inferior leads II, III and aVF; and inverted V3-V6
- P wave morphology is consistent throughout
Related Topics
References
- Poutiainen AM et al. Prevalence and natural course of ectopic atrial tachycardia. Eur Heart J. 1999 May;20(9):694-700
- Buttà C et al. Electrocardiographic diagnosis of atrial tachycardia: classification, P-wave morphology, and differential diagnosis with other supraventricular tachycardias. Ann Noninvasive Electrocardiol. 2015 Jul;20(4):314-27
Advanced Reading
Online
- Wiesbauer F, Kühn P. ECG Mastery: Yellow Belt online course. Understand ECG basics. Medmastery
- Wiesbauer F, Kühn P. ECG Mastery: Blue Belt online course: Become an ECG expert. Medmastery
- Kühn P, Houghton A. ECG Mastery: Black Belt Workshop. Advanced ECG interpretation. Medmastery
- Rawshani A. Clinical ECG Interpretation ECG Waves
- Smith SW. Dr Smith’s ECG blog.
- Wiesbauer F. Little Black Book of ECG Secrets. Medmastery PDF
Textbooks
- Zimmerman FH. ECG Core Curriculum. 2023
- Mattu A, Berberian J, Brady WJ. Emergency ECGs: Case-Based Review and Interpretations, 2022
- Straus DG, Schocken DD. Marriott’s Practical Electrocardiography 13e, 2021
- Brady WJ, Lipinski MJ et al. Electrocardiogram in Clinical Medicine. 1e, 2020
- Mattu A, Tabas JA, Brady WJ. Electrocardiography in Emergency, Acute, and Critical Care. 2e, 2019
- Hampton J, Adlam D. The ECG Made Practical 7e, 2019
- Kühn P, Lang C, Wiesbauer F. ECG Mastery: The Simplest Way to Learn the ECG. 2015
- Grauer K. ECG Pocket Brain (Expanded) 6e, 2014
- Surawicz B, Knilans T. Chou’s Electrocardiography in Clinical Practice: Adult and Pediatric 6e, 2008
- Chan TC. ECG in Emergency Medicine and Acute Care 1e, 2004
LITFL Further Reading
- ECG Library Basics – Waves, Intervals, Segments and Clinical Interpretation
- ECG A to Z by diagnosis – ECG interpretation in clinical context
- ECG Exigency and Cardiovascular Curveball – ECG Clinical Cases
- 100 ECG Quiz – Self-assessment tool for examination practice
- ECG Reference SITES and BOOKS – the best of the rest
ECG LIBRARY
Emergency Physician in Prehospital and Retrieval Medicine in Sydney, Australia. He has a passion for ECG interpretation and medical education | ECG Library |
MBBS DDU (Emergency) CCPU. Adult/Paediatric Emergency Medicine Advanced Trainee in Melbourne, Australia. Special interests in diagnostic and procedural ultrasound, medical education, and ECG interpretation. Co-creator of the LITFL ECG Library. Twitter: @rob_buttner


“Both atrial flutter and multifocal atrial tachycardia are specific types of atrial tachycardia.” – is this correct?
If you’re using the term atrial tachycardia as synonymous with ectopic atrial tachycardia or focal atrial tachycardia then I don’t think this is right as atrial flutter is a distinct and separate entity.
Hi Luke,
Thank you for your comment. Atrial tachycardia is a broader term referring to any SVT initiated outside of the sinus node, and comprises FAT, MAT and atrial flutter. Atrial flutter is a separate entity to FAT but they are both forms of atrial tachycardia.
I hope this helps.
Rob
Hello there
I’m just curious as to why example 2 is considered tachycardia if the rate is 95.
My thoughts are with the rate, inverted P waves, and borderline prolonged QRS that this would be considered an accelerated junctional rhythm. If the impulse originated from the AV nodal area it would have to travel back up the atria (causing the inverted P wave in lead II) and it would also have a prolonged or borderline prolonged QRS.
-Narrow complex rhythm; QRS duration < 120ms (unless pre-existing bundle branch block or rate-related aberrant conduction)
-Ventricular rate usually 60 – 100 bpm
-Retrograde P waves may be present and can appear before, during or after the QRS complex
-Retrograde P waves are usually inverted in the inferior leads (II, III, aVF), upright in aVR + V1.
(https://litfl.com/accelerated-junctional-rhythm-ajr/)
I look forward to your response.
Could example 1 be junctional tachycardia due to the short P-R interval?