Accelerated Junctional Rhythm (AJR)
Accelerated Junctional Rhythm Overview
Accelerated junctional rhythm (AJR) occurs when the rate of an AV junctional pacemaker exceeds that of the sinus node. This situation arises when there is increased automaticity in the AV node coupled with decreased automaticity in the sinus node.
ECG Features of AJR
- Narrow complex rhythm; QRS duration < 120ms (unless pre-existing bundle branch block or rate-related aberrant conduction)
- Ventricular rate usually 60 – 100 bpm
- Retrograde P waves may be present and can appear before, during or after the QRS complex. They are usually inverted in inferior leads (II, III, aVF), upright in aVR + V1
- AV dissociation may be present with the ventricular rate usually greater than the atrial rate
- There may be associated ECG features of digoxin effect or digoxin toxicity

Causes of Accelerated Junctional Rhythm
Anything that disrupts electrical activity in the SA node can precipitate AJR. Common causes include:
- Digoxin toxicity (= the classic cause of AJR)
- Beta-agonists, e.g. isoprenaline, adrenaline
- Myocardial ischaemia
- Myocarditis
- Cardiac surgery
Terminology
Junctional rhythms are arbitrarily classified by their rate:
- Junctional bradycardia: < 40 bpm
- Junctional Escape Rhythm: 40-60 bpm
- Accelerated Junctional Rhythm: 60-100 bpm
- Junctional Tachycardia: > 100 bpm
They may also be classified by aetiology:
- Automatic Junctional Rhythms (e.g. AJR) = Due to enhanced automaticity in AV nodal cells
- Re-entrant Junctional Rhythms (e.g. AVNRT) = Due to re-entrant loop involving AV node
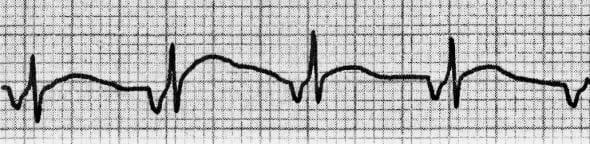
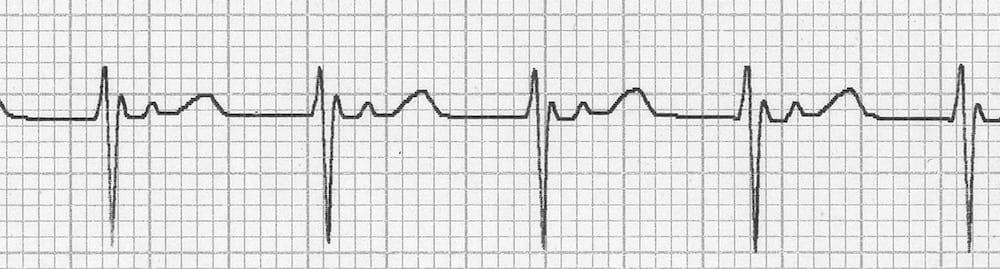
Differential Diagnosis of AJR
Rapid AJR may be difficult to distinguish from re-entrant junctional tachycardias such as AVNRT or AVRT.
- Irregularity of rhythm and heart-rate variability are suggestive of automatic junctional tachycardia
- Automatic junctional tachycardia is typically non-responsive to vagal manoeuvres — there may be some transient slowing of the ventricular rate but reversion to sinus rhythm will not occur
NOTE: AJR with aberrant conduction may be difficult to distinguish from accelerated idioventricular rhythm. The presence of fusion or capture beats indicates a ventricular rather than junctional focus.
ECG Examples
Example 1
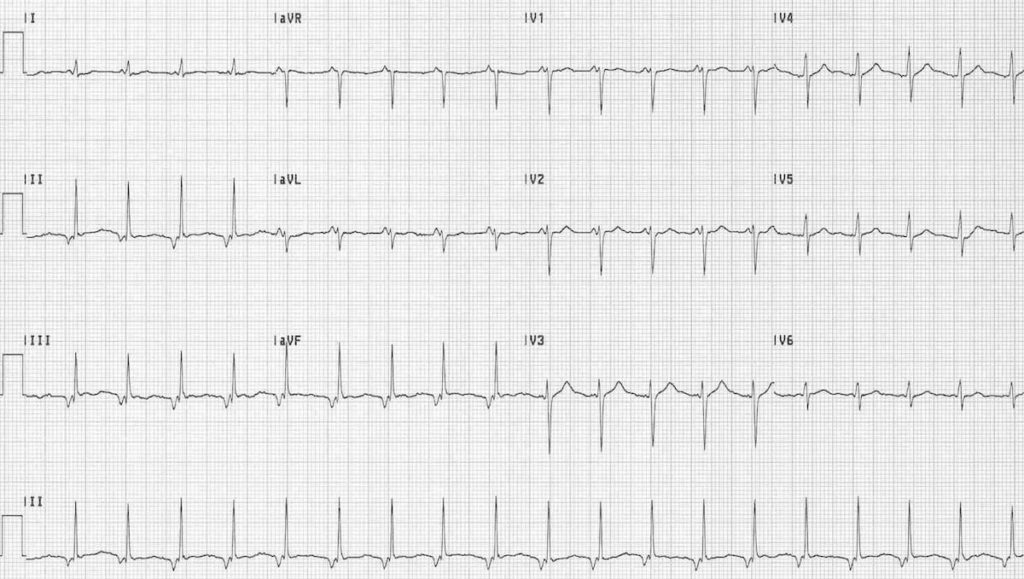
Junctional Tachycardia
- Narrow complex tachycardia at 115 bpm
- Retrograde P waves — inverted in II, III and aVF; upright in V1 and aVR
- Short PR interval (< 120 ms) indicates a junctional rather than atrial focus
Related Topics
- AV nodal re-entry tachycardia (AVNRT)
- Atrioventricular re-entry tachycardia (AVRT)
- Accelerated idioventricular rhythm (AIVR)
References
- Dr Smith’s ECG Blog – Accelerated Junctional Rhythm
- JJ Larkin’s ECG of the Week – Accelerated Junctional Rhythm
Advanced Reading
Online
- Wiesbauer F, Kühn P. ECG Mastery: Yellow Belt online course. Understand ECG basics. Medmastery
- Wiesbauer F, Kühn P. ECG Mastery: Blue Belt online course: Become an ECG expert. Medmastery
- Kühn P, Houghton A. ECG Mastery: Black Belt Workshop. Advanced ECG interpretation. Medmastery
- Rawshani A. Clinical ECG Interpretation ECG Waves
- Smith SW. Dr Smith’s ECG blog.
- Wiesbauer F. Little Black Book of ECG Secrets. Medmastery PDF
Textbooks
- Zimmerman FH. ECG Core Curriculum. 2023
- Mattu A, Berberian J, Brady WJ. Emergency ECGs: Case-Based Review and Interpretations, 2022
- Straus DG, Schocken DD. Marriott’s Practical Electrocardiography 13e, 2021
- Brady WJ, Lipinski MJ et al. Electrocardiogram in Clinical Medicine. 1e, 2020
- Mattu A, Tabas JA, Brady WJ. Electrocardiography in Emergency, Acute, and Critical Care. 2e, 2019
- Hampton J, Adlam D. The ECG Made Practical 7e, 2019
- Kühn P, Lang C, Wiesbauer F. ECG Mastery: The Simplest Way to Learn the ECG. 2015
- Grauer K. ECG Pocket Brain (Expanded) 6e, 2014
- Surawicz B, Knilans T. Chou’s Electrocardiography in Clinical Practice: Adult and Pediatric 6e, 2008
- Chan TC. ECG in Emergency Medicine and Acute Care 1e, 2004
LITFL Further Reading
- ECG Library Basics – Waves, Intervals, Segments and Clinical Interpretation
- ECG A to Z by diagnosis – ECG interpretation in clinical context
- ECG Exigency and Cardiovascular Curveball – ECG Clinical Cases
- 100 ECG Quiz – Self-assessment tool for examination practice
- ECG Reference SITES and BOOKS – the best of the rest
ECG LIBRARY
Emergency Physician in Prehospital and Retrieval Medicine in Sydney, Australia. He has a passion for ECG interpretation and medical education | ECG Library |
MBBS DDU (Emergency) CCPU. Adult/Paediatric Emergency Medicine Advanced Trainee in Melbourne, Australia. Special interests in diagnostic and procedural ultrasound, medical education, and ECG interpretation. Co-creator of the LITFL ECG Library. Twitter: @rob_buttner

