
Joe Vincent Meigs
Joe Vincent Meigs (1892-1963) American gynaecologic oncology. Meigs syndrome, radical hysterectomy innovations and validation of Pap smear screening.

Joe Vincent Meigs (1892-1963) American gynaecologic oncology. Meigs syndrome, radical hysterectomy innovations and validation of Pap smear screening.

Swiss ophthalmologist Johann Friedrich Horner (1831–1886), eponym of Horner's syndrome, advanced ophthalmic surgery and neuroanatomical diagnostics
Demetrius Chilaiditi (1883–1975) Austrian born radiologist. Described Chilaiditi sign (1910); details of his life remain largely undocumented.
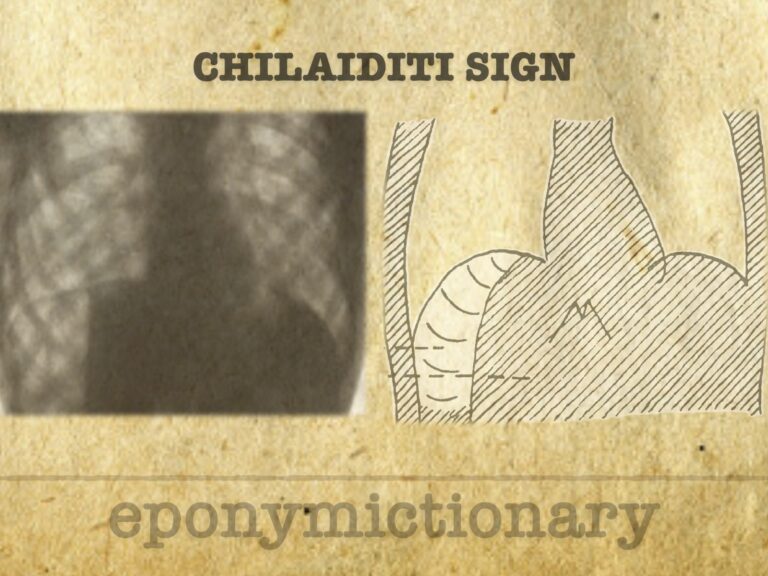
Chilaiditi sign: rare condition with bowel loops interposed between liver and diaphragm, with symptoms (syndrome). Must differentiate from free air.

Saint’s Triad: coexistence of hiatal hernia, colonic diverticulosis, and gallstones—now linked to connective tissue disorders like herniosis.

Charles FM Saint (1886–1973), pioneer of South African surgery, identified Saint’s triad and shaped generations through surgical teaching and aphorisms.
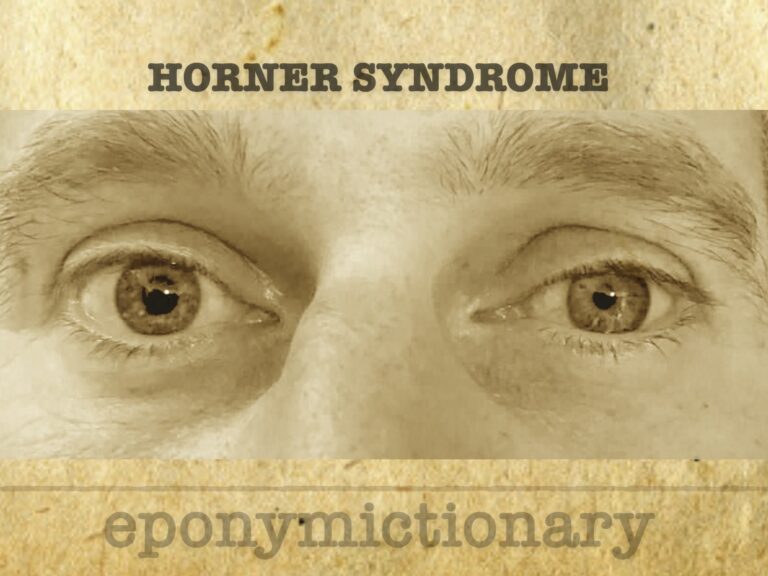
Horner syndrome is associated with an interruption to the sympathetic nerve supply of the eye. It is characterized by the classic triad of miosis, partial ptosis, and anhidrosis +/- enophthalmos
Hickam’s Dictum reminds clinicians that patients may have multiple diseases, challenging Occam’s Razor in diagnostic reasoning and medical education.

John B. Hickam (1914–1970), physician and educator, led IU’s Dept of Medicine and inspired “Hickam’s dictum” challenging diagnostic simplicity.

Jerome W. Conn (1907–1994) American endocrinologist. Described Conn syndrome (primary aldosteronism), transforming the diagnosis of hypertension.

A. F. Stanley Kent (1863–1958), cardiac physiologist; 'bundle of Kent', shaped early electrophysiology; pioneered industrial fatigue science

Frieda Robscheit-Robbins (1888–1973), pioneering pathologist who advanced aneamia research, yet was overlooked for the 1934 Nobel despite major contributions.