ECG Case 016
20-year old patient with sudden onset of palpitations. What does the ECG show?
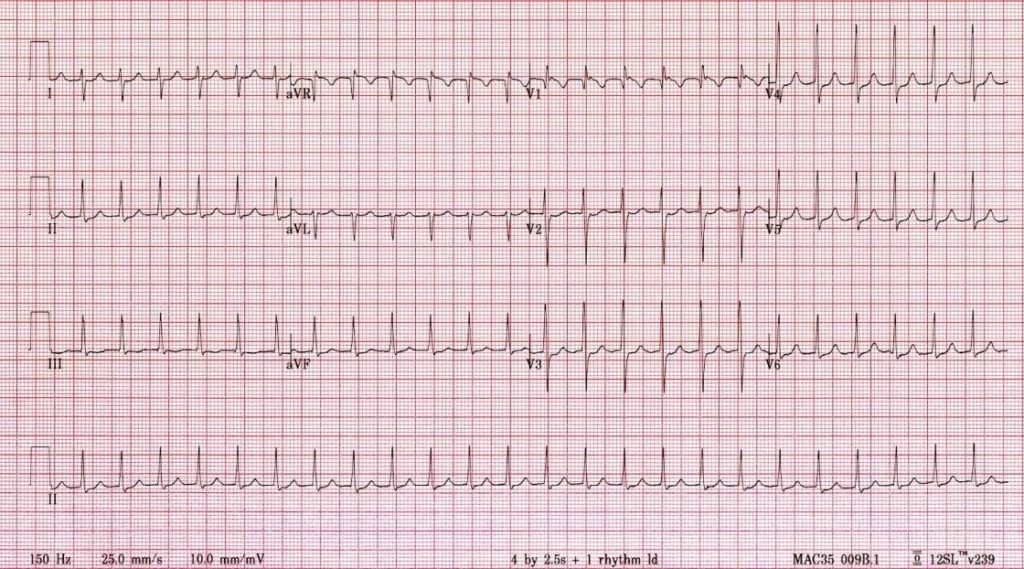
Describe and interpret this ECG
ECG ANSWER and INTERPRETATION
Main Abnormalities
- Narrow complex tachycardia at ~ 150 bpm
- Right axis deviation = just rightward of +90 degrees
- Pseudo-R’ waves in V1-2 = retrograde P waves superimposed on the terminal QRS causing peaking of the J-point
- No clear sinus P waves or flutter waves seen
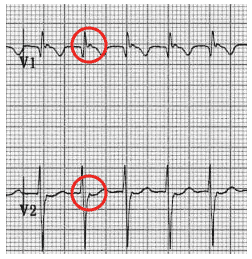
Pseudo R’ waves
CLINICAL PEARLS
Differential Diagnosis
When you see a regular narrow complex tachycardia at 150 bpm, you should think of four main diagnoses:
- Atrial flutter with 2:1 block (especially in elderly, IHD, CCF)
- AV-nodal reentry tachycardia (“SVT”)
- Orthodromic AV reentry tachycardia in WPW
- Sinus tachycardia — should see P waves but may be hidden in the T waves (e.g. with concurrent 1st degree AV block). There should also be some HR variability compared to the other 3 rhythms
The patient’s young age and presence of retrograde P waves (pseudo R’ waves) suggest a paroxysmal reentry tachycardia involving the AV node — either AVNRT (“SVT”) or orthodromic AVRT.
The next step is a therapeutic trial of vagal maneouvres and/or adenosine… (see Quiz ECG 017).
References
Further Reading
- Wiesbauer F, Kühn P. ECG Mastery: Yellow Belt online course. Understand ECG basics. Medmastery
- Wiesbauer F, Kühn P. ECG Mastery: Blue Belt online course: Become an ECG expert. Medmastery
- Kühn P, Houghton A. ECG Mastery: Black Belt Workshop. Advanced ECG interpretation. Medmastery
- Rawshani A. Clinical ECG Interpretation ECG Waves
- Smith SW. Dr Smith’s ECG blog.
- Wiesbauer F. Little Black Book of ECG Secrets. Medmastery PDF
TOP 100 ECG Series
Emergency Physician in Prehospital and Retrieval Medicine in Sydney, Australia. He has a passion for ECG interpretation and medical education | ECG Library |
