
SimCase 002
SimCase 002: older patient with severe hypercapnia and respiratory distress. Explore ventilator setup, escalation, and troubleshooting.

SimCase 002: older patient with severe hypercapnia and respiratory distress. Explore ventilator setup, escalation, and troubleshooting.

Stigler’s Law of Eponymy: no discovery is named after its true originator. Explore its history, Merton’s roots, and modern scientific misattribution.

Sir William Broadbent (1835–1907), British physician-neurologist; pioneer in hemiplegia theory, neurosyphilis and the pericardial Broadbent sign.

Out-Sleep the Competition. The 80/20 Guide to Owning the Night. We work against biology. Against light. Against clock time.
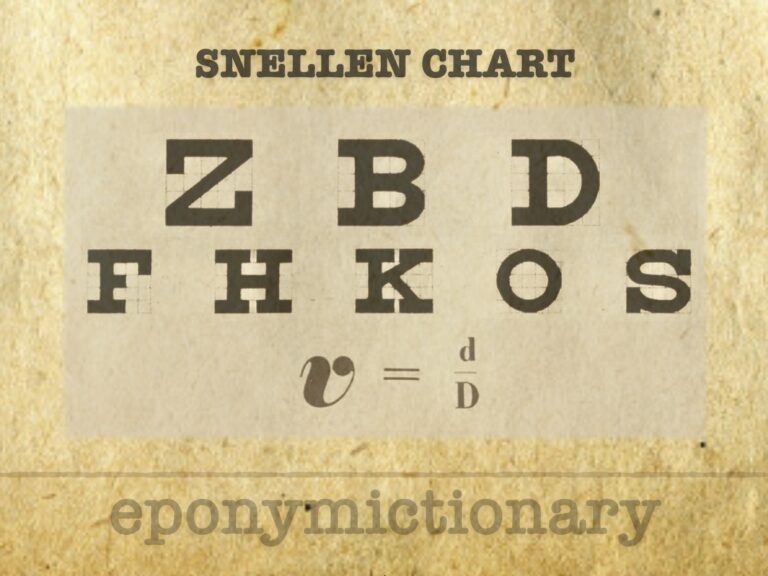
Snellen chart: history of visual acuity testing from Hooke to ETDRS, with key milestones, optotype design, and contributions from Snellen, Donders, Sloan

Critical Care SimCase 001: febrile patient with severe hypoxaemia and acidaemia. Work through ventilator setup, escalation, and troubleshooting.

Greta Beighton (1939–2017), English nurse and genetic researcher who co-developed the Beighton Score for joint hypermobility and contributed to clinical genetics in South Africa.

The Beighton Score is a simple, numerical index which is used to express the range and severity of joint movements in normal and affected persons.

Peter Beighton (1934–2023) was a clinical geneticist known for research on inherited skeletal disorders and co-developing the Beighton Score for joint hypermobility.

Mary Clayton Holt (1924-1993), English cardiologist. Holt-Oram syndrome (1960); pioneer in cardiac rehab and advocate for women in medicine.

Out-Sleep the Competition. The Top ten tips to attain the 80/20 of elite sleep. The Pareto Principle for peak performance.
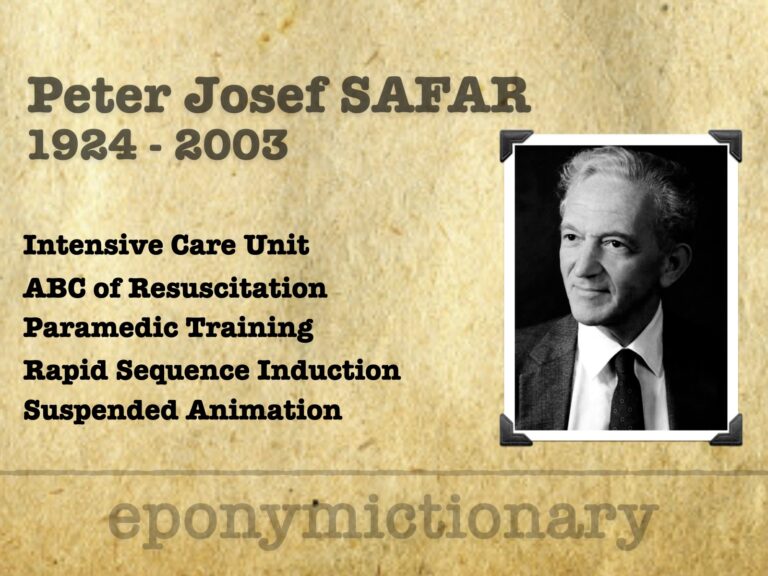
Peter Safar (1924–2003), father of modern resuscitation, pioneered CPR, ICUs, paramedic training, and therapeutic hypothermia.