Wolff–Parkinson–White syndrome
Wolff-Parkinson-White (WPW) Syndrome is a combination of the presence of a congenital accessory pathway and episodes of tachyarrhythmia.

Wolff-Parkinson-White (WPW) Syndrome is a combination of the presence of a congenital accessory pathway and episodes of tachyarrhythmia.

In patients with AF and pre-excitation, the presence of an accessory pathway allows for rapid AV conduction, with a risk of degeneration into VT and VF

Tachyarrhythmia that occurs in patients with accessory pathways, due to formation of a re-entry circuit between the AV node and accessory pathway

Wolff-Parkinson-White (WPW) Syndrome is a combination of the presence of a congenital accessory pathway and episodes of tachyarrhythmias

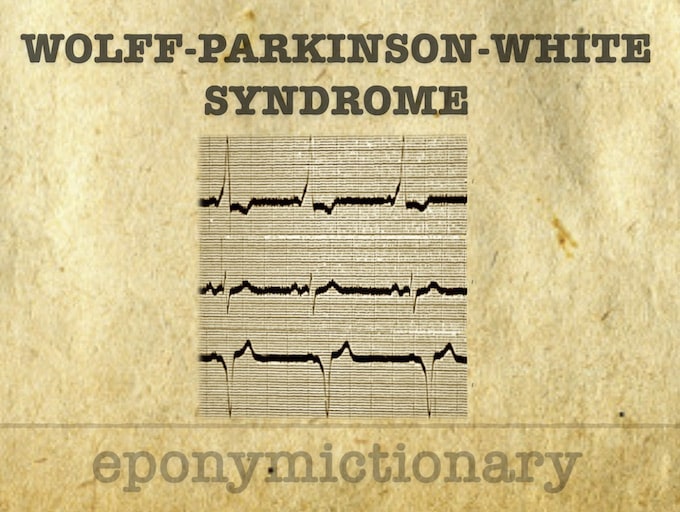
The characteristic ECG findings in the Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome include a slurred upstroke to the QRS complex (the Delta wave)

Paul Dudley White (1886-1973) was an American cardiologist. White with Louis Wolff and John Parkinson (WPW syndrome 1930); McGinn-White pattern (1935)

Sir John Parkinson (1885-1976) was an English cardiologist. In 1930, Parkinson along with Louis Wolff and Paul Dudley White, described WPW Syndrome

Louis Wolff (1898-1972) was an American cardiologist. Eponymously affiliated with the Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome (WPW) described in 1930

20 yr old female who presented to the Emergency Department following an episode of chest pain. At review she was pain free and all vital signs were normal. Her serial ECG's are below, there is ~30 mins between each ECG.

35 yr old male who presented to the Emergency Department complaining of palpitations, dyspnoea, and lightheadedness. Describe and interpret this ECG. LITFL Top 100 ECG

William Francis 'Fran' Ganong Jr. (1924 – 2007) was an American physiologist. Eponym: Lown-Ganong-Levine (1952)

Lown–Ganong–Levine syndrome (LGL): Proposed pre-excitation syndrome. Accessory pathway composed of James fibres.