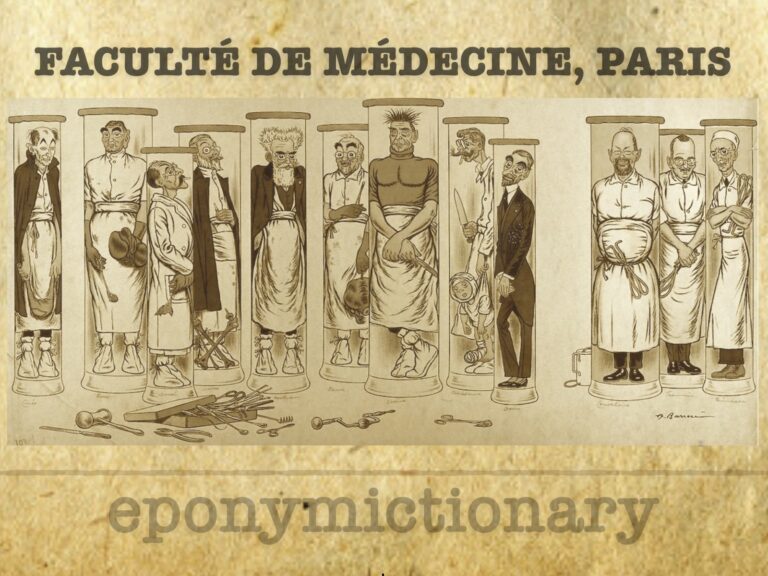
A Cluster of Surgeons
Adrien Barrère (1874-1931) produced a series of lithographs of the Professors in the Faculties of Medicine. Fourth lithograph 'A cluster of surgeons' in 1910

Adrien Barrère (1874-1931) produced a series of lithographs of the Professors in the Faculties of Medicine. Fourth lithograph 'A cluster of surgeons' in 1910
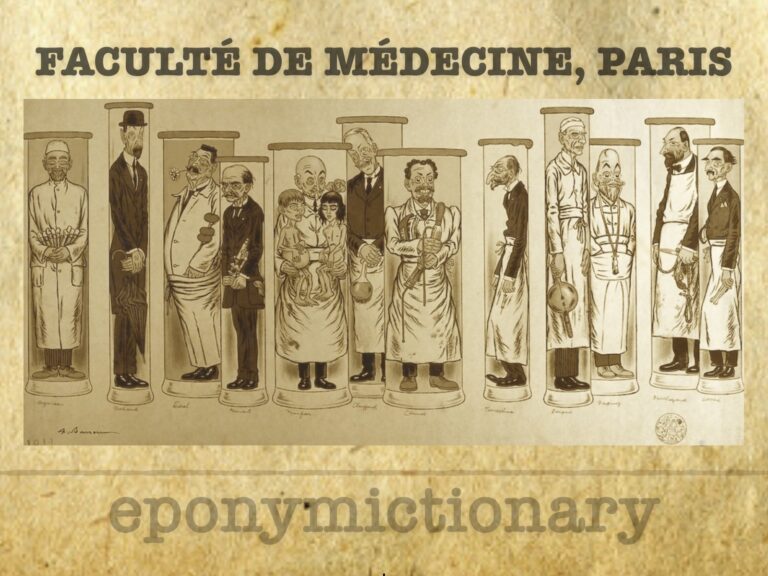
Adrien Barrère (1874-1931) produced a series of lithographs of the Professors in the Faculties of Medicine. Third lithograph 'Twelve Professors of Pathology' in 1910

Adrien Barrère (1874-1931) produced a series of lithographs of the Professors in the Faculties of Medicine. Second lithograph '16 French doctors' in 1906

Adrien Barrère (1874-1931) produced a series of lithographs of the Professors in the Faculties of Medicine. First lithograph 'a vivid grouping' in 1903

Adrien Barrère (Adrien Baneux) (1874-1931) was a French medical caricaturist, poster artist and painter in Paris during the Belle Époque
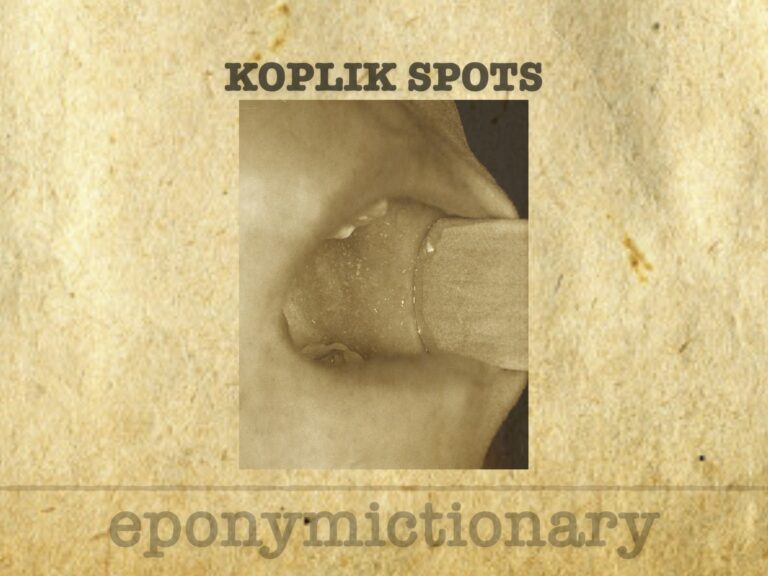
Koplik spots are pathognomonic buccal lesions in early measles, first described by Henry Koplik in 1896, aiding pre-rash diagnosis and outbreak control.
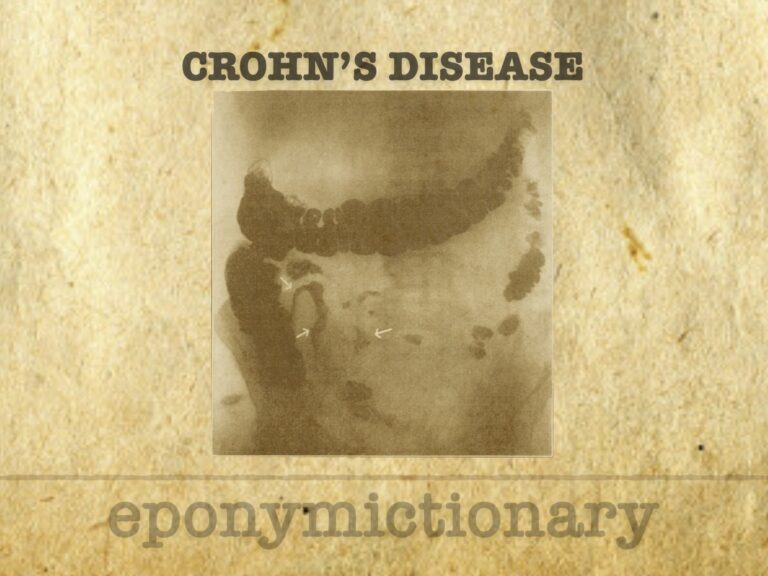
Chronic inflammatory bowel disease affecting the GI tract, Crohn’s disease was first defined in 1932 but described decades earlier by Dalziel and others

EGPA (Churg–Strauss syndrome): rare ANCA-associated vasculitis with asthma, eosinophilia, and systemic granulomatous inflammation of small vessels
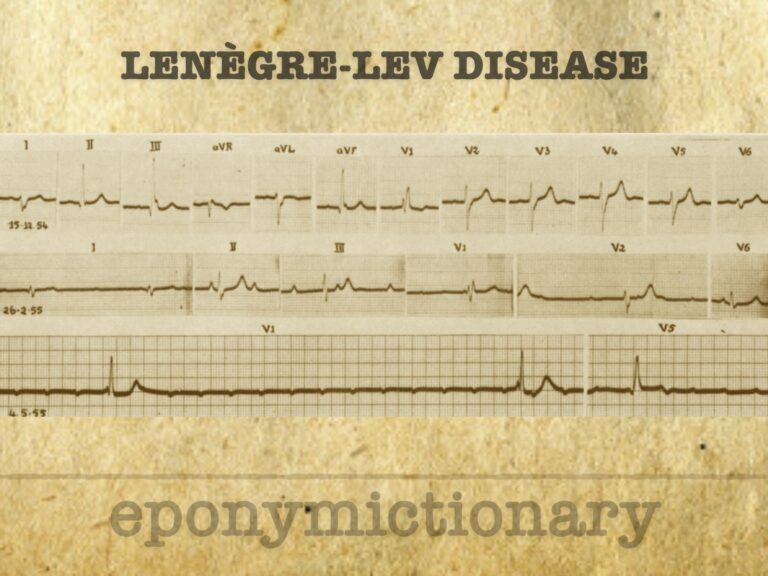
Acquired fibrous degeneration of the left and right bundle branches, eventually manifesting as permanent complete atrioventricular (AV) dissociation with cardiac pauses and Adams-Stokes attacks

Stokes-Adams syndrome is an abrupt, transient loss of consciousness due to a sudden but pronounced decrease in the cardiac output

Cheyne-Stokes respiration is a cyclical breathing pattern of apnoea and hyperpnoea, seen in heart failure, brain injury, and end-of-life settings.
May–Thurner syndrome (MTS). Venous compression syndrome causing left-sided iliofemoral DVT, first anatomically defined by May and Thurner in 1957.