
Janeway lesions
Janeway lesions; painless, haemorrhagic macules of the palms/soles linked to infective endocarditis. Edward Gamaliel Janeway (1899)

Janeway lesions; painless, haemorrhagic macules of the palms/soles linked to infective endocarditis. Edward Gamaliel Janeway (1899)

Guillain-Barré syndrome is the most common and severe acute inflammatory paralytic neuropathy. The classical description of GBS involves rapidly progressive bilateral weakness, usually starting in the distal lower extremities and ascending proximally.

Bell’s palsy: Acute idiopathic unilateral paralysis of the facial nerve. Named after Sir Charles Bell and his description in 1827

Pancoast Tumour is a primary bronchogenic carcinoma which arises in the apex of the lung at the superior pulmonary sulcus.

Pancoast Syndrome occurs secondary to local compression of brachial plexus and sympathetic chain by superior (pulmonary) sulcus tumors.

Wernicke encephalopathy is an acute, reversible encephalopathy caused by thiamine deficiency, classically presenting with ophthalmoplegia, ataxia, and confusion.
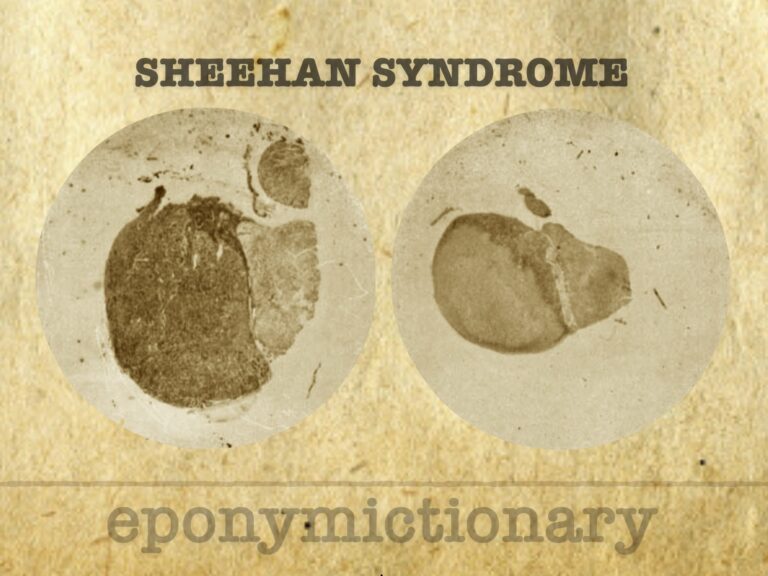
Postpartum hypopituitarism following ischaemic necrosis of the anterior pituitary gland. Pituitary necrosis occurs secondary to hypophyseal portal vessel thrombosis following significant postpartum haemorrhage, hypovolemia, and shock.
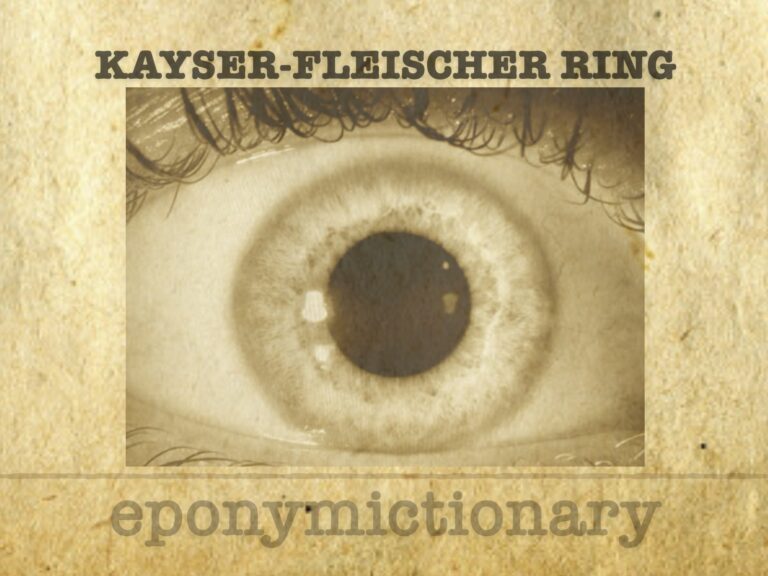
corneal ring at the level of Descemet’s membrane, caused by copper deposition in the cornea. It is a cardinal sign of Wilson’s disease (hepatolenticular degeneration)

Parry-Romberg syndrome: progressive facial hemiatrophy usually involving the soft tissues of one side of the face. Parry (1825) Romberg (1846)

Peutz-Jeghers-syndrome: A Syndrome gastrointestinal polyposis characterized by specific melanin pigmentations of the skin and mucous membranes
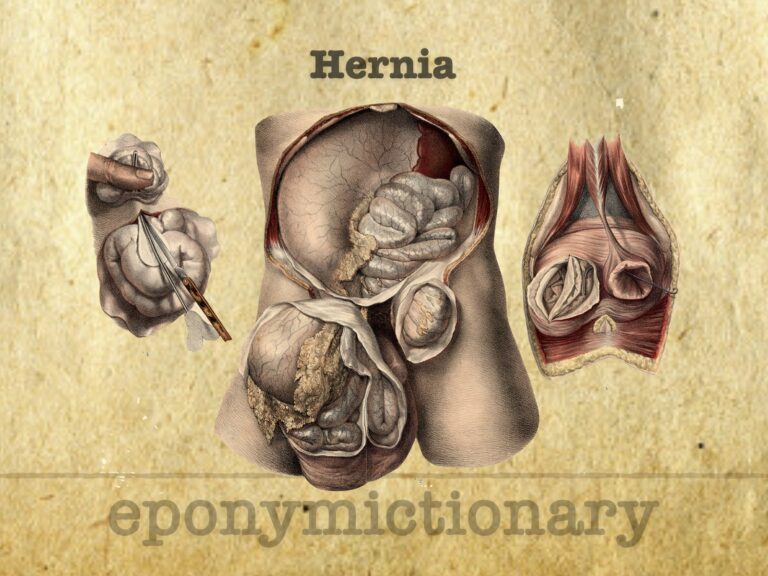
Eponymous hernias: clear definition, etymology, and a quick guide to types—Amyand, de Garengeot, Littre, Richter, Spigelian, Bochdalek, Morgagni.

Lower brachial plexus injury, with consequent weakness and wasting of the C8–T1 musculature. Augusta Klumpke (1859-1927)