ECG Case 033
75-year old patient presenting with acute dyspnoea, productive cough and wheeze. Describe the ECG.
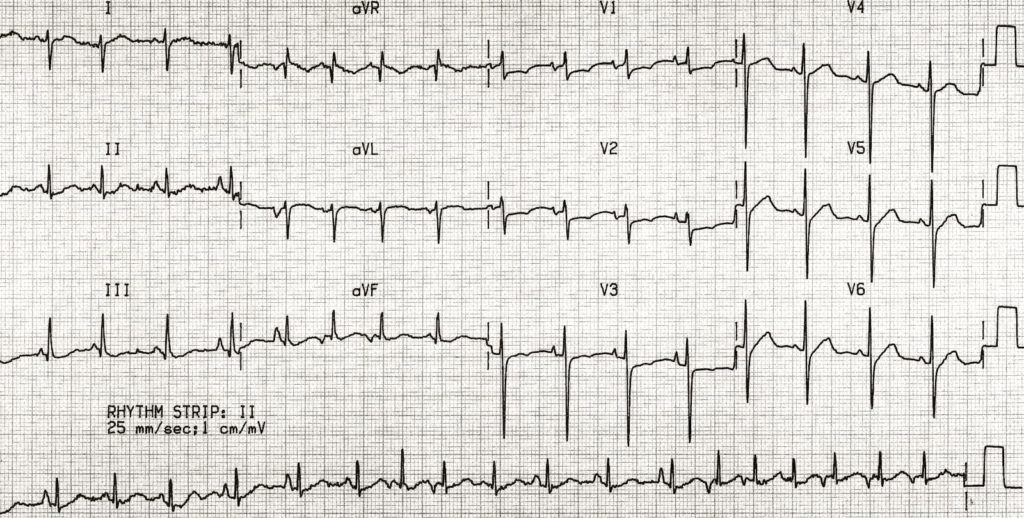
Describe and interpret this ECG
ECG ANSWER and INTERPRETATION
Main Abnormalities
- Irregularly irregular narrow-complex tachycardia at ~ 110 bpm
- At least 3 different P wave morphologies seen in the lead II rhythm strip, indicating multiple foci of activity within the atria
- No flutter or fibrillatory waves — rules out AF or flutter with variable block
- Evidence of right ventricular hypertrophy — RAD, dominant R wave in V1, deep S wave in V6
Diagnosis
The combination of…
- Irregular narrow-complex tachycardia (> 100 bpm)
- Multifocal atrial activity (3 or more distinct P wave morphologies)
- No evidence of flutter / AF
… is diagnostic of multifocal atrial tachycardia (MAT).
ECG changes of right ventricular hypertrophy may represent cor pulmonale due to COPD.
CLINICAL PEARLS
Clinical Significance
MAT typically occurs in patients with severe COPD, as the final common pathway of multiple arrhythmogenic mechanisms:
- Right atrial dilatation (from cor pulmonale)
- Increased sympathetic drive — due to hypoxia / hypercarbia
- Bronchodilators — beta-agonist, theophylline
- Electrolyte abnormalities; hypokalaemia and hypomagnesaemia (e.g. secondary to diuretics / beta-agonists)
MAT typically resolves with treatment of the underlying COPD exacerbation and correction of any electrolyte abnormalities, although it may evolve into AF or flutter.
References
Further Reading
- Wiesbauer F, Kühn P. ECG Mastery: Yellow Belt online course. Understand ECG basics. Medmastery
- Wiesbauer F, Kühn P. ECG Mastery: Blue Belt online course: Become an ECG expert. Medmastery
- Kühn P, Houghton A. ECG Mastery: Black Belt Workshop. Advanced ECG interpretation. Medmastery
- Rawshani A. Clinical ECG Interpretation ECG Waves
- Smith SW. Dr Smith’s ECG blog.
- Wiesbauer F. Little Black Book of ECG Secrets. Medmastery PDF
TOP 100 ECG Series
Emergency Physician in Prehospital and Retrieval Medicine in Sydney, Australia. He has a passion for ECG interpretation and medical education | ECG Library |
MBBS DDU (Emergency) CCPU. Adult/Paediatric Emergency Medicine Advanced Trainee in Melbourne, Australia. Special interests in diagnostic and procedural ultrasound, medical education, and ECG interpretation. Co-creator of the LITFL ECG Library. Twitter: @rob_buttner

