
Suspended animation
Suspended animation is defined as the therapeutic induction of a state of tolerance to temporary complete systemic ischaemia

Suspended animation is defined as the therapeutic induction of a state of tolerance to temporary complete systemic ischaemia

Pierre Marie (1853–1940), French neurologist and endocrinologist; defined acromegaly, described progressive aphasia, and helped shape modern neurology.

Pharmacology of Semaglutide, the Glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) receptor agonist. Incretin mimetic and Antidiabetic agent

Jean-Alexandre Barré (1880–1967). French neurologist ; co-described Guillain–Barré syndrome; pioneer in vestibular neurology and semiology; eponyms include Barré test and Barré–Liéou syndrome.

Critical evaluation of continuous infusion of beta-lactam antibiotics (rather than intermittent dosing) in critically ill patients.

William Halsted (1852–1922), pioneering American surgeon, revolutionized surgery with aseptic technique, anesthesia, gloves, and the residency training model.

Xray and ultrasound (POCUS) evaluation of integrity of quadriceps tendon, patella tendon, and patella evaluating for tendon rupture and patella fracture.

Meigs syndrome: Triad of ascites with hydrothorax in association with benign ovarian tumor, that is cured after tumor resection. Described in 1934 by Joe Vincent Meigs (1892-1963)

Joe Vincent Meigs (1892-1963) American gynaecologic oncology. Meigs syndrome, radical hysterectomy innovations and validation of Pap smear screening.

Swiss ophthalmologist Johann Friedrich Horner (1831–1886), eponym of Horner's syndrome, advanced ophthalmic surgery and neuroanatomical diagnostics
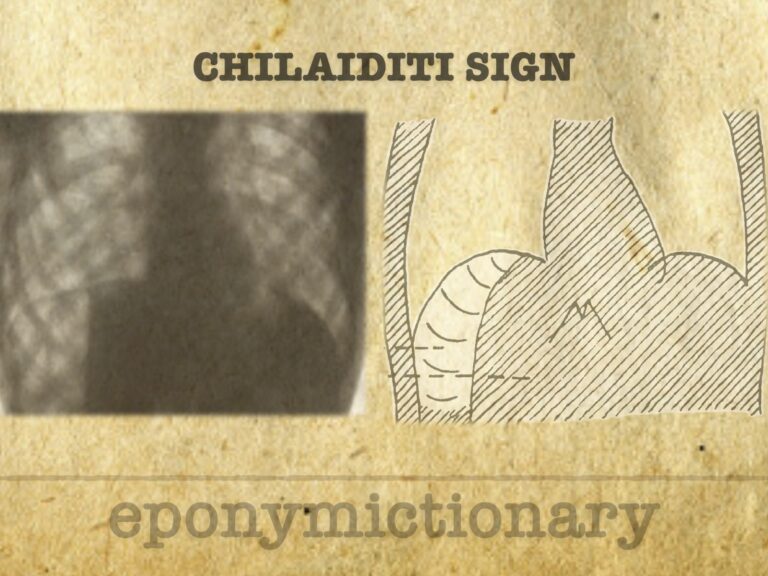
Chilaiditi sign: rare condition with bowel loops interposed between liver and diaphragm, with symptoms (syndrome). Must differentiate from free air.
Demetrius Chilaiditi (1883–1975) Austrian born radiologist. Described Chilaiditi sign (1910); details of his life remain largely undocumented.