
William B. Schwartz
William B. Schwartz (1922–2009) American nephrologist. Co-described SIADH, pioneered decision theory, medical AI, and ethical health care rationing.

William B. Schwartz (1922–2009) American nephrologist. Co-described SIADH, pioneered decision theory, medical AI, and ethical health care rationing.
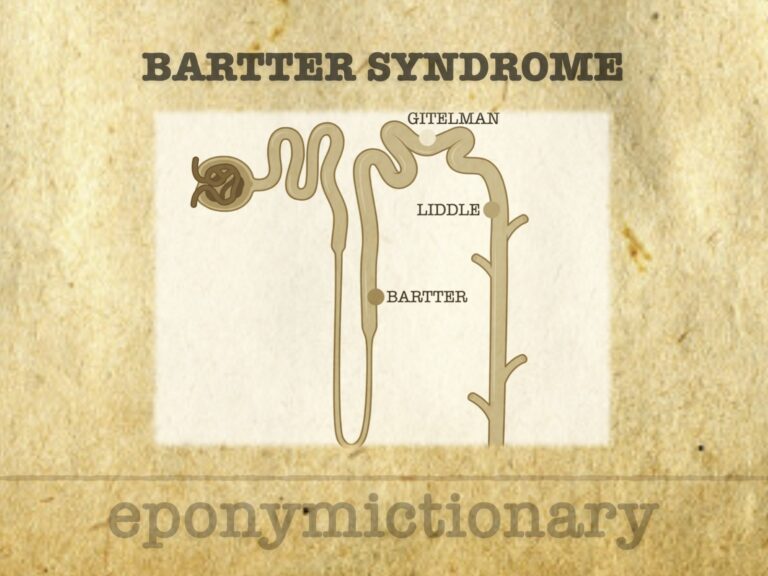
Bartter Syndrome: Renal tubulopathy with hypokalaemic alkalosis, high renin and aldosterone, normal BP, and polyuria—mimics loop diuretic effect at the thick ascending limb.

Frederic Crosby Bartter (1914–1983) American endocrinologist. Defined Bartter syndrome, co-described SIADH, and advanced adrenal and renal physiology.

Crawford W. Long (1815–1878), American physician who first used sulphuric ether for surgical anaesthesia on March 30, 1842

Augustus Desiré Waller (1856–1922) was a British physiologist who recorded the first human electrocardiogram (ECG) in 1887. His work laid the foundation for modern electrocardiography and inspired Willem Einthoven’s innovations.

Brain Herniation Syndromes. Clinical and radiological assessment of 13 cases. Neuroimaging case study series with Teresa Crow, Troy Carnwath, Scott DiMeo, L. Erin Miller and Natalie Rall

Erich Seidel (1882–1946), German ophthalmologist. Described Seidel scotoma (1914): sickle/arcuate blind-spot extension in early glaucoma.

Mogens Stig Norn (1925–2023), Danish ophthalmologist. Introduced lissamine green vital staining (1973); chief editor Acta Ophthalmologica (1975–88).

Manuel Straub (1858–1916), Dutch ophthalmologist. Early human fluorescein corneal staining (1888) and landmark lens-induced uveitis work

Lester T. Jones (1894/95–1983), Oregon ophthalmologist. Defined the lacrimal pump, created Jones fluorescein dye tests, and pioneered CDCR with the Jones tube.
Theodore Ernst Obrig (1894–1967) pioneered cobalt-blue and fluorescein viewing (1938), transforming contact lens fitting and corneal surface assessment.

Paul Ehrlich (1854–1915), German physician. Pioneer of chemotherapy; fluorescein eye studies, immunology, and Salvarsan for syphilis.