
Mogens Norn
Mogens Stig Norn (1925–2023), Danish ophthalmologist. Introduced lissamine green vital staining (1973); chief editor Acta Ophthalmologica (1975–88).

Mogens Stig Norn (1925–2023), Danish ophthalmologist. Introduced lissamine green vital staining (1973); chief editor Acta Ophthalmologica (1975–88).

Manuel Straub (1858–1916), Dutch ophthalmologist. Early human fluorescein corneal staining (1888) and landmark lens-induced uveitis work

Lester T. Jones (1894/95–1983), Oregon ophthalmologist. Defined the lacrimal pump, created Jones fluorescein dye tests, and pioneered CDCR with the Jones tube.
Theodore Ernst Obrig (1894–1967) pioneered cobalt-blue and fluorescein viewing (1938), transforming contact lens fitting and corneal surface assessment.

Paul Ehrlich (1854–1915), German physician. Pioneer of chemotherapy; fluorescein eye studies, immunology, and Salvarsan for syphilis.

Ernst Pflüger (1846–1903), Swiss ophthalmologist. Early fluorescein cornea experiments (1882) and influential work on refraction, optotypes and colour vision testing

Henrik Sjögren (1899–1986), Swedish ophthalmologist. Defined keratoconjunctivitis sicca and described Sjögren syndrome; introduced 1% rose bengal staining (1933).

On Call 4th Edition: practical, symptom-based, risk-stratified handbook for ward calls in Australasia & UK. Updated, expanded, and evidence-based.
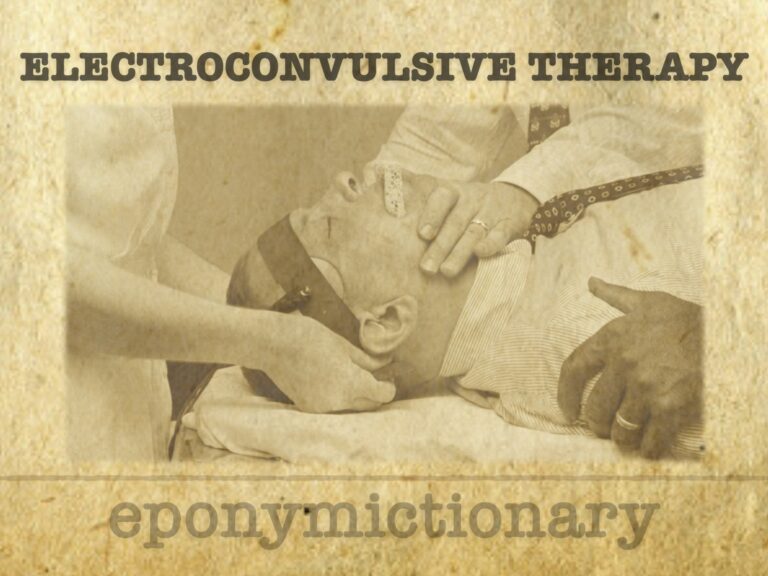
Electroconvulsive therapy (ECT): history, pioneers, modern use, efficacy, and controversy, one of psychiatry’s most enduring treatments.

Own the Hamilton: video guide to transitioning from Oxylog to Hamilton T1. Learn manual strategies, ASV, and simulation-based ventilator training.

Dominique-Jean Larrey (1766–1842), Napoleon’s surgeon, pioneered flying ambulances, triage, and humane battlefield care, earning admiration from all sides.

Emergency Procedure, instruction and discussion: Haematoma block; used in forearm or distal radius fracture requiring reduction