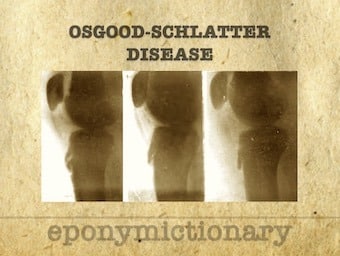
Osgood-Schlatter disease
Osgood–Schlatter disease (OSD) Osteochondrosis or traction apophysitis of the tibial tubercle. Paget (1891), Osgood (1903), Schlatter (1903)

Osgood–Schlatter disease (OSD) Osteochondrosis or traction apophysitis of the tibial tubercle. Paget (1891), Osgood (1903), Schlatter (1903)
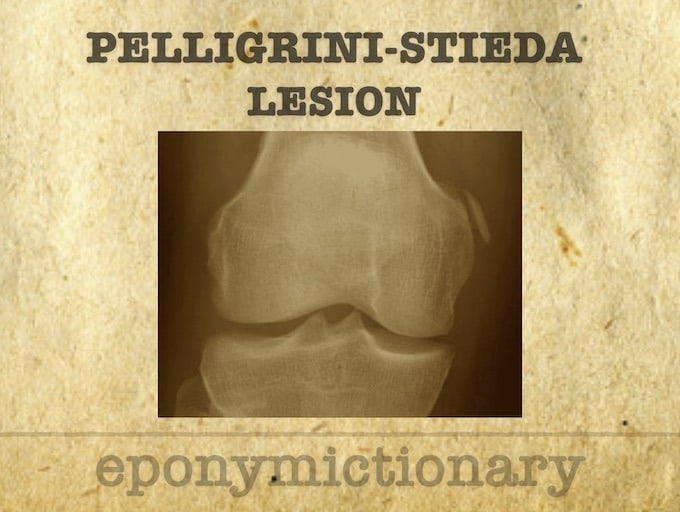
Köhler-Pellegrini-Stieda lesion: ossification near medial femoral collateral ligament adjacent to the margin of the medial femoral condyle.

Bundgaard et al introduced us in 2018 to "Familial ST-segment depression syndrome", a new cardiac arrhythmia syndrome predisposing to atrial fibrillation, VT, and sudden cardiac death.

In 2008, Haïssaguerre et al challenged the well-embedded term "benign" early repolarization by demonstrating a link between this familiar ECG pattern and idiopathic VF arrest

Aslanger et al identified a specific ECG pattern concerning for acute inferior occlusion MI in patients with concomitant multi-vessel disease, that does not display contiguous ST-segment elevation or fulfil STEMI criteria
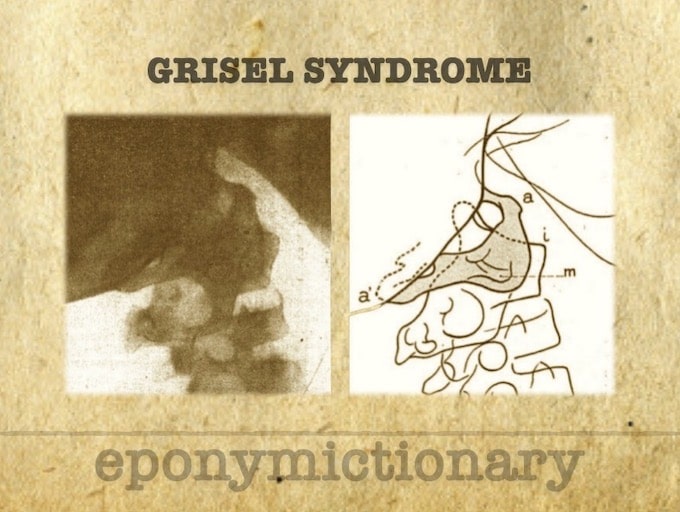
Spontaneous, nontraumatic rotatory subluxation of the atlantoaxial joint following peripharyngeal inflammation or ENT surgical procedures

Köhler disease: rare, self-limiting, avascular necrosis (osteochondrosis) of the navicular bone in children. Described in 1908 by Alban Köhler (1874–1947)
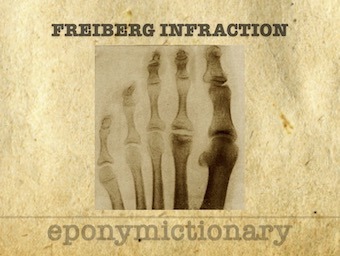
Freiberg infraction: osteochondrosis of the metatarsal heads (typically the 2nd metatarsal head) described by Albert Freiberg in 1914, Alban Köhler in 1915

Menière’s disease is a condition characterized by the triad of episodic vertigo, tinnitus, and hearing loss, caused by endolymphatic hydrops of the labyrinthine system of the inner ear.

Dressler beat: Specifically a 'ventricular fusion beat' in the presence of paroxysmal ventricular tachycardia. Wide complex tachycardia with VT

Reactive arthritis [archaic eponym: Reiter's syndrome] systemic, seronegative spondyloarthropathy secondary to a precipitating infection.

Ludwig angina: rapidly progressive gangrenous bilateral cellulitis of the submandibular space with risk of life-threatening airway compromise. 1836 - Wilhem Frederick von Ludwig was the first to clearly describe this disorder and differentiate it from other types of 'inflammation' in the neck.