Colles fracture
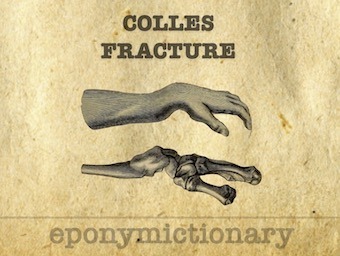
Colles fracture: Extra-articular fracture of the distal radius with dorsal angulation of the distal fragment. Abraham Colles (1814)

Colles fracture: Extra-articular fracture of the distal radius with dorsal angulation of the distal fragment. Abraham Colles (1814)
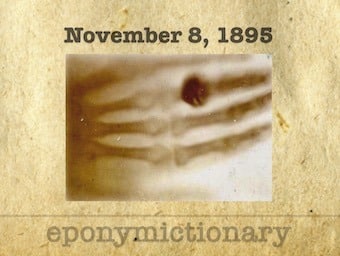
On November 8, 1895 Wilhelm Röntgen, chair of physics at Würzburg, noted an unusual phenomenon, that would change the world of medicine

Bryant’s sign: Scrotal ecchymosis associated with ruptured abdominal aortic aneurysm (AAA) first described in 1903 by John Henry Bryant (1867-1906)
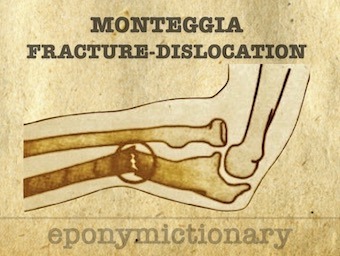
Monteggia fracture. Fracture of the proximal or middle third of the ulna with associated radial head dislocation/instability. GB Monteggia 1812

Galeazzi fracture (1934). Fracture of the distal third of the radius with associated Distal radio-ulna joint (DRUJ) disruption.

Naxos disease: a recessively inherited condition with arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia/ cardiomyopathy (ARVD/C) non-epidermolytic palmoplantar keratoderma, and woolly hair
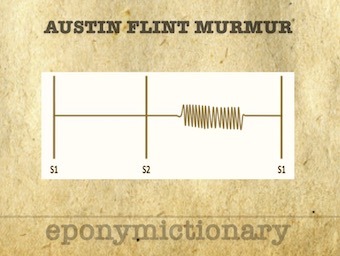
Austin Flint Murmur: Mid diastolic, low pitch rumble heard best at the apex. Absence of opening snap/loud S1 distinguishes from that of mitral stenosis

Primary thrombosis of the subclavian vein at the costoclavicular junction. The formation of an axillo-subclavian vein thrombosis results from endothelial trauma, often as a result of repetitive activity of the upper limbs.

Seldinger Technique a technique for safe percutaneous access to vessels and hollow organs that is widely used today. Sven Ivar Seldinger (1921 – 1998)

In 1894, Morison published his anatomic description of the hepatorenal space; its role in the surgical treatment of gallbladder disease; and proposed the value of postoperative drainage of that space.

Löffler (Loeffler) syndrome is a transient, self-limiting, and benign pulmonary eosinophilia, characterised by pulmonary opacities on X-ray, elevated blood eosinophils and an acute onset of potential symptoms of mainly cough and dyspnoea.

In 1961, Jack Handyside Barnes, his nine year-old son, and a local surf lifesaver were rushed to Cairns Base Hospital after developing Irukandji syndrome.