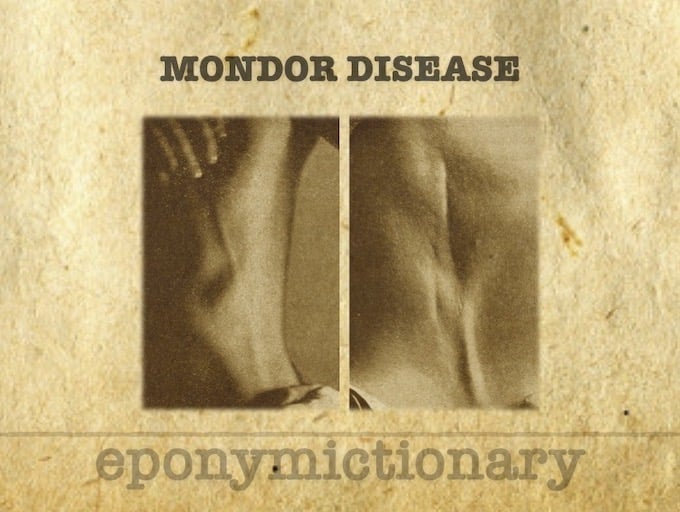
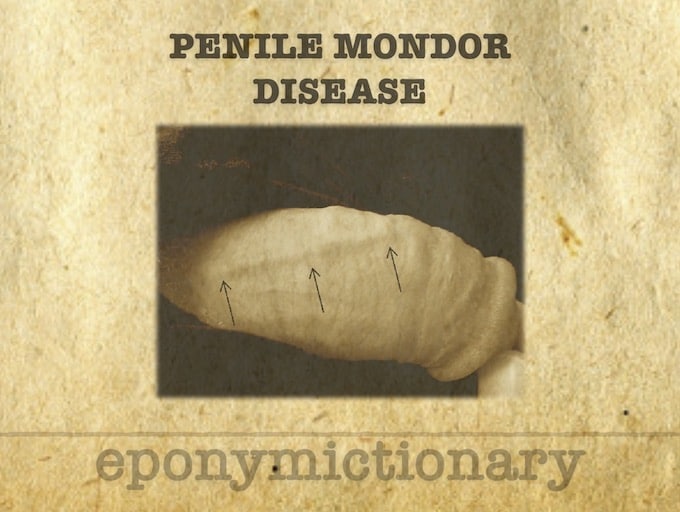
Forestier disease
Diffuse idiopathic skeletal hyperostosis (DISH), the now more generally accepted name for Forestier disease; is a poorly understood, systemic condition characterised by progressive calcification and ossification of ligaments and entheses