
AF Stanley Kent
A. F. Stanley Kent (1863–1958), cardiac physiologist; 'bundle of Kent', shaped early electrophysiology; pioneered industrial fatigue science

A. F. Stanley Kent (1863–1958), cardiac physiologist; 'bundle of Kent', shaped early electrophysiology; pioneered industrial fatigue science

Frieda Robscheit-Robbins (1888–1973), pioneering pathologist who advanced aneamia research, yet was overlooked for the 1934 Nobel despite major contributions.
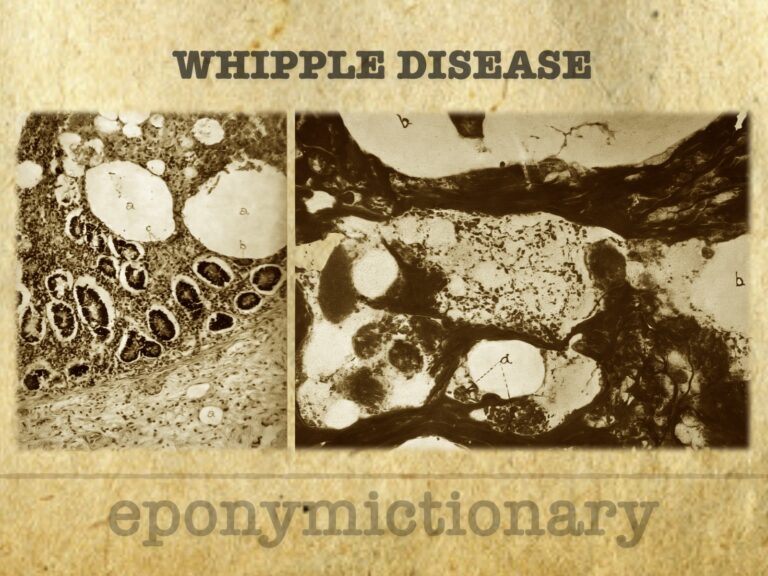
Whipple disease: rare systemic infection by Tropheryma whipplei. Explore its history, diagnosis, and treatment from 1907 discovery to present day

Swiss paediatrician Guido Fanconi (1892–1979) defined Fanconi anaemia and Fanconi syndrome, shaping modern paediatrics and medical genetics.

George Hoyt Whipple (1878–1976), Nobel winner, advanced anaemia therapy, coined thalassaemia, and described Whipple disease in 1907.

Hamilton T1 paediatric/neonatal ventilation cards: SIMV+, NIV, nCPAP strategies with weight-based titration and troubleshooting guidance.

Hamilton T1 adult/paediatric ventilation cards: SIMV+, NIV, ASV strategies with settings, titration and troubleshooting for critical care.

Pablo Mirizzi (1893–1964), Argentine surgeon who pioneered intraoperative cholangiography and described Mirizzi syndrome of biliary duct compression
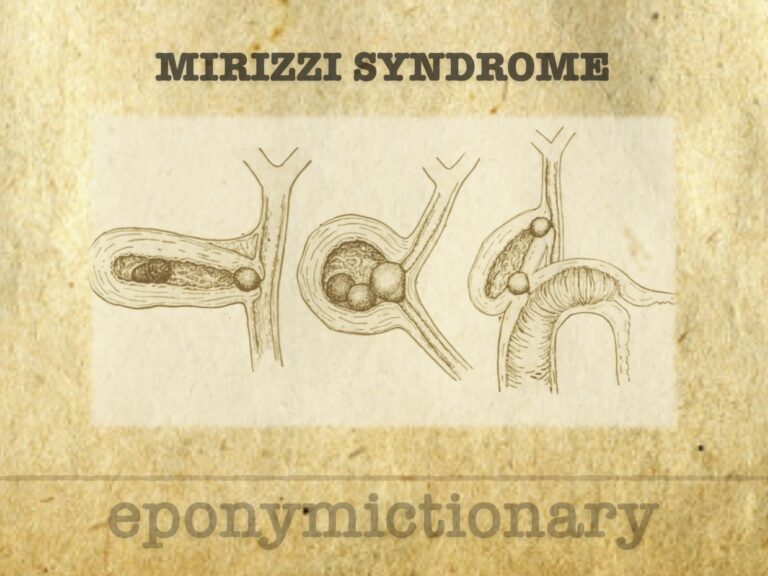
Mirizzi syndrome is a rare complication of gallstone disease involving bile duct compression or fistula formation, with evolving classifications from Mirizzi to Csendes and Beltrán

Mark M. Ravitch, pioneering pediatric surgeon, innovator of the Ravitch procedure, stapling, intussusception care, and Cantrell’s sequence.

William John Adie (1886 – 1935) was an Australian neurologist. Best known for describing the tonically dilated pupil (Adie pupil) associated with absent deep tendon reflexes (Adie syndrome) and his description of narcolepsy

Irish neurologist Sir Gordon Holmes (1876–1965), pioneer of cerebellar and visual pathway research, key wartime studies, and enduring neurological eponym