
Dieulafoy Lesion
Dieulafoy’s lesion: minute gastric erosion over a large arteriole, causing massive GI bleeding. First defined as exulceratio simplex in 1898.

Dieulafoy’s lesion: minute gastric erosion over a large arteriole, causing massive GI bleeding. First defined as exulceratio simplex in 1898.

Georges Dieulafoy (1839–1911), French physician, pioneer of gastroenterology; remembered for Dieulafoy lesion, triad(s), and aspirator

Eugen von Bamberger (1858–1921), Austrian internist; co-described Marie–Bamberger syndrome (hypertrophic pulmonary osteoarthropathy); pioneer of clinical diagnostics.
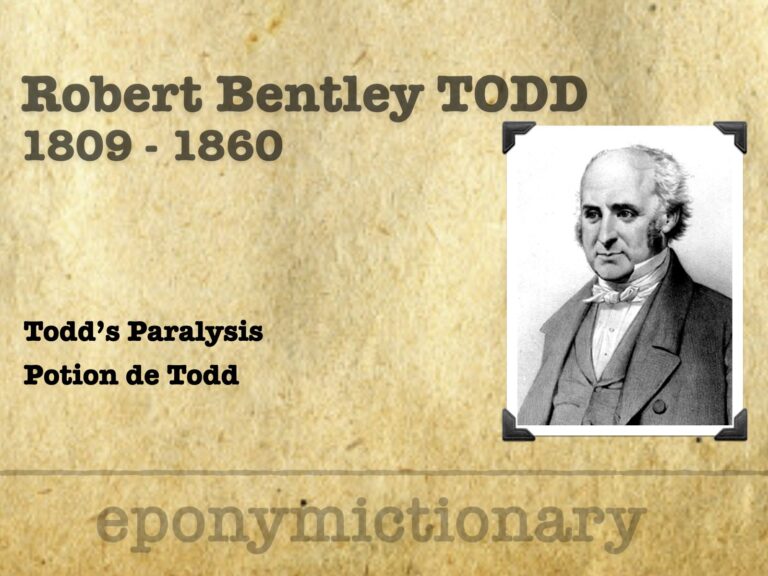
Robert Bentley Todd (1809-1860) was an Irish physician. Provided early depictions of migraine, peripheral neuritis, and postepileptic paralysis (Todd's palsy). He also gave an important discourse on locomotor ataxy (tabes dorsalis).
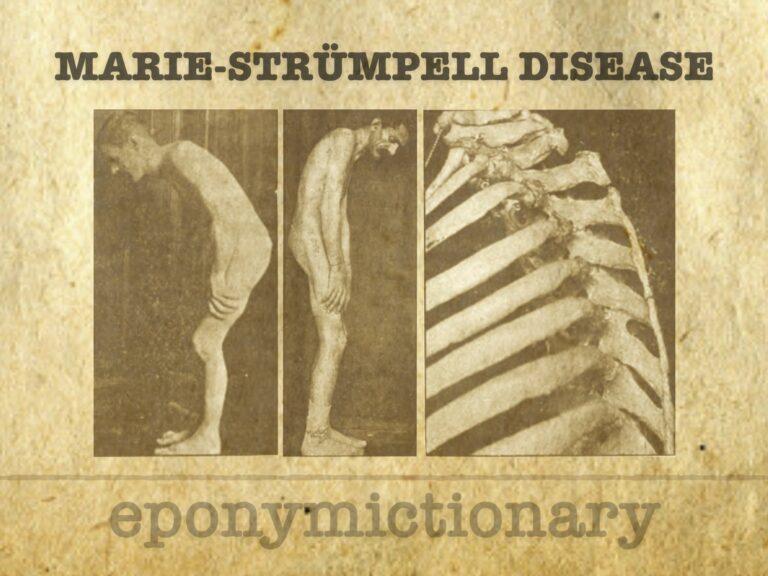
Marie-Strümpell disease (ankylosing spondylitis): a chronic inflammatory spinal arthritis with progressive axial fusion, first described by Pierre Marie and Adolf Strümpell in the late 19th century.

Sylvester McGinn (1904–1984); American cardiologist; McGinn-White sign (S1Q3T3) in pulmonary embolism; pioneer in Boston cardiac care and research.

Moritz Heinrich Romberg (1795–1873) a founder of clinical neurology, Romberg’s sign, Parry–Romberg syndrome and Howship–Romberg sign
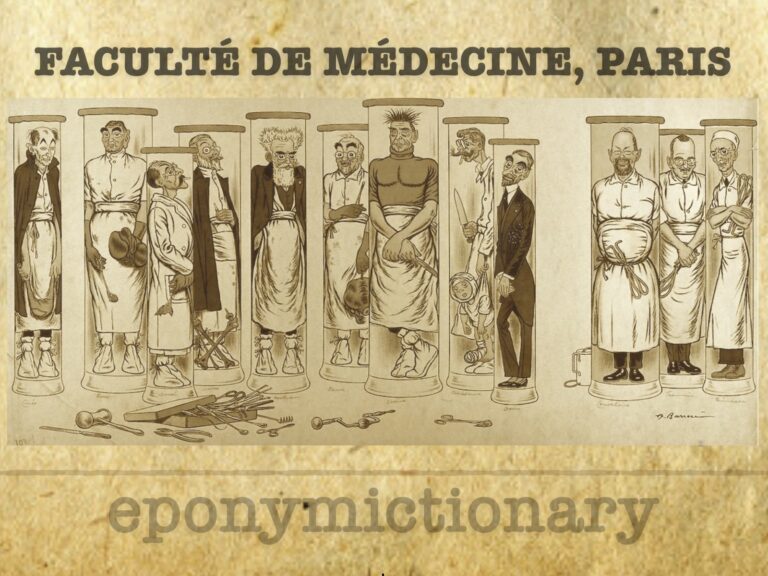
Adrien Barrère (1874-1931) produced a series of lithographs of the Professors in the Faculties of Medicine. Fourth lithograph 'A cluster of surgeons' in 1910
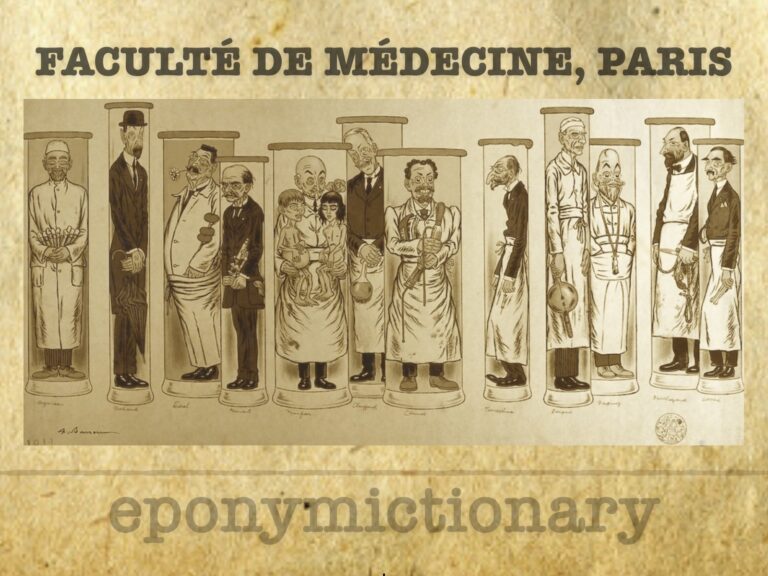
Adrien Barrère (1874-1931) produced a series of lithographs of the Professors in the Faculties of Medicine. Third lithograph 'Twelve Professors of Pathology' in 1910

Adrien Barrère (1874-1931) produced a series of lithographs of the Professors in the Faculties of Medicine. Second lithograph '16 French doctors' in 1906

Adrien Barrère (1874-1931) produced a series of lithographs of the Professors in the Faculties of Medicine. First lithograph 'a vivid grouping' in 1903

Adrien Barrère (Adrien Baneux) (1874-1931) was a French medical caricaturist, poster artist and painter in Paris during the Belle Époque