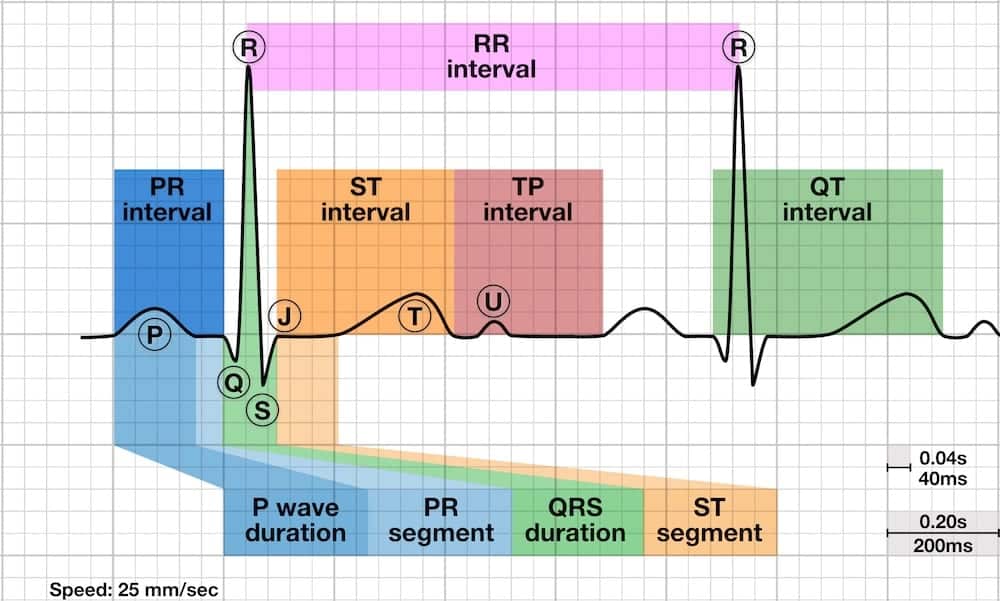
PR segment
The PR segment is the flat, usually isoelectric segment between the end of the P wave and the start of the QRS complex.
PR segment abnormalities
These occur in two main conditions:
- Pericarditis
- Atrial ischaemia
Pericarditis
The characteristic changes of acute pericarditis are:
- PR segment depression.
- Widespread concave (‘saddle-shaped’) ST elevation.
- Reciprocal ST depression and PR elevation in aVR and V1
- Absence of reciprocal ST depression elsewhere.
NB. PR segment changes are relative to the baseline formed by the T-P segment.
Typical ECG of acute pericarditis.
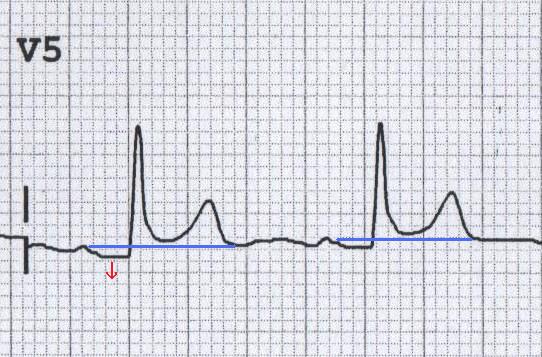
PR segment depression in V5 due to acute pericarditis (note also some concave ST elevation)
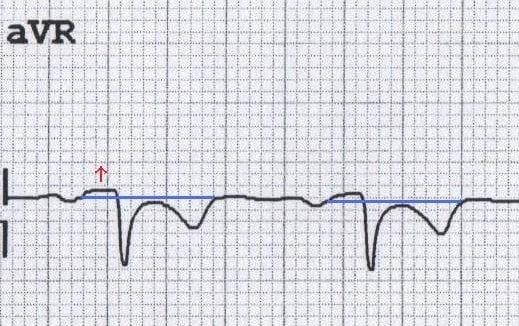
PR elevation in aVR due to acute pericarditis (note the reciprocal ST depression)
Atrial ischaemia
- PR segment elevation or depression in patients with myocardial infarction indicates concomitant atrial ischaemia or infarction.
- This finding has been associated with poor outcomes following MI, increased risk for the development of atrioventricular block, supraventricular arrhythmias and cardiac free-wall rupture.
Liu’s criteria for diagnosing atrial ischaemia / infarction include:
- PR elevation >0.5 mm in V5 & V6 with reciprocal PR depression in V1 & V2
- PR elevation >0.5 mm in lead I with reciprocal PR depression in leads II & III
- PR depression >1.5 mm in the precordial leads
- PR depression >1.2 mm in leads I, II, & III
- Abnormal P wave morphology: M-shaped,W-shaped,irregular,or notched (minor criteria)
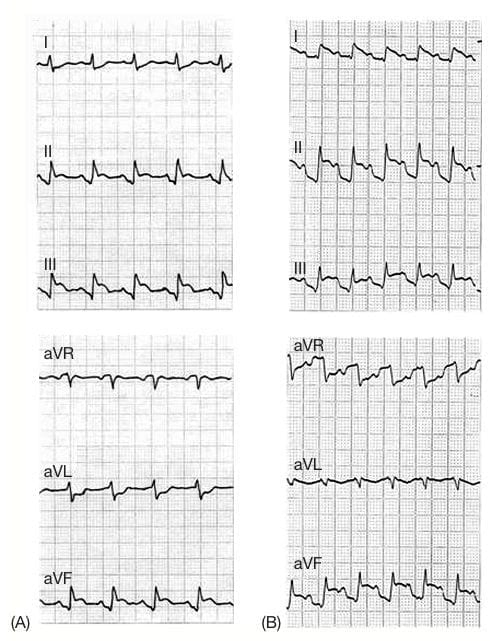
PR depression in inferior STEMI indicating concomitant atrial infarction
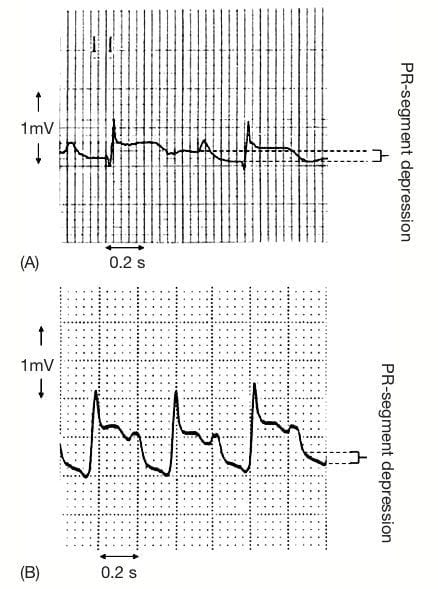
Profound PR-segment depression in inferior leads: (A) with clear-cut TP segment; and (B) without clear-cut TP segment; in acute inferior myocardial infarction. Note also ST-segment elevation in inferior leads. (Reproduced from Jim et al.)
Measurement of PR depression
- Measurement of PR-segment depression: (A) with clear-cut TP segment; and (B) without clear-cut TP segment. (Reproduced from Jim et al.)
References
- Jim MH, Siu CW, Chan AO, Chan RH, Lee SW, Lau CP. Prognostic implications of PR-segment depression in inferior leads in acute inferior myocardial infarction. Clin Cardiol. 2006 Aug;29(8):363-8
ECG Library Basics
Advanced Reading
Online
- Wiesbauer F, Kühn P. ECG Mastery: Yellow Belt online course. Understand ECG basics. Medmastery
- Wiesbauer F, Kühn P. ECG Mastery: Blue Belt online course: Become an ECG expert. Medmastery
- Kühn P, Houghton A. ECG Mastery: Black Belt Workshop. Advanced ECG interpretation. Medmastery
- Rawshani A. Clinical ECG Interpretation ECG Waves
- Smith SW. Dr Smith’s ECG blog.
- Wiesbauer F. Little Black Book of ECG Secrets. Medmastery PDF
Textbooks
- Zimmerman FH. ECG Core Curriculum. 2023
- Mattu A, Berberian J, Brady WJ. Emergency ECGs: Case-Based Review and Interpretations, 2022
- Straus DG, Schocken DD. Marriott’s Practical Electrocardiography 13e, 2021
- Brady WJ, Lipinski MJ et al. Electrocardiogram in Clinical Medicine. 1e, 2020
- Mattu A, Tabas JA, Brady WJ. Electrocardiography in Emergency, Acute, and Critical Care. 2e, 2019
- Hampton J, Adlam D. The ECG Made Practical 7e, 2019
- Kühn P, Lang C, Wiesbauer F. ECG Mastery: The Simplest Way to Learn the ECG. 2015
- Grauer K. ECG Pocket Brain (Expanded) 6e, 2014
- Surawicz B, Knilans T. Chou’s Electrocardiography in Clinical Practice: Adult and Pediatric 6e, 2008
- Chan TC. ECG in Emergency Medicine and Acute Care 1e, 2004
LITFL Further Reading
- ECG Library Basics – Waves, Intervals, Segments and Clinical Interpretation
- ECG A to Z by diagnosis – ECG interpretation in clinical context
- ECG Exigency and Cardiovascular Curveball – ECG Clinical Cases
- 100 ECG Quiz – Self-assessment tool for examination practice
- ECG Reference SITES and BOOKS – the best of the rest
ECG LIBRARY