Acute Kidney Injury
Reviewed and revised 7 August 2015
OVERVIEW
- AKI is the entire spectrum of disease (mild -> severe), and can be defined as an abrupt (1 to 7 days) and sustained (more than 24 hours) decrease in kidney function
- Mortality of critically patients with acute renal failure is high (50%–60%)
- Renal recovery in survivors may be as high as 90% but as many as 50% of survivors do not return to baseline function
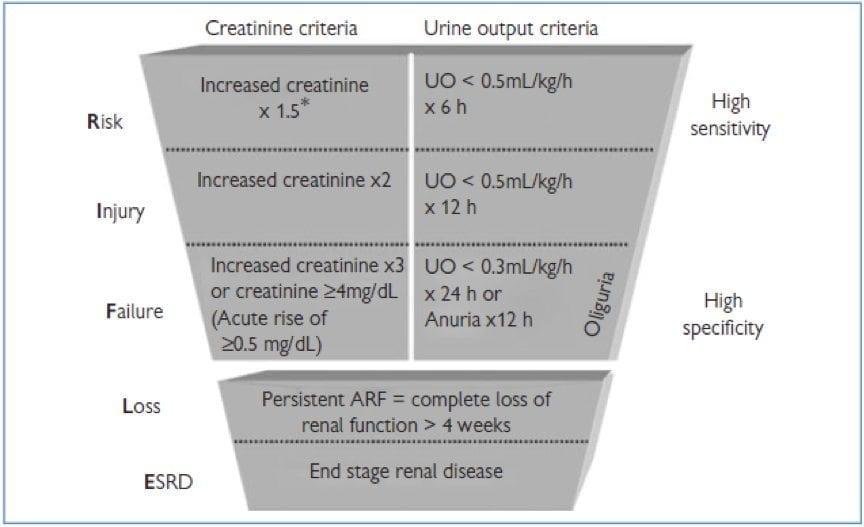
Spectrum as classified according to the RIFLE criteria
- Risk
- Injury
- Failure
- Loss
- End-stage
INCIDENCE + PROGRESSION
- common (35-65%) of ICU admissions
- 5-20% general hospital admissions
- mortality significantly increases in patients with AKI
RISK FACTORS
- sepsis
– > age (especially > 62 years) - race (black)
– > severity in APACHE III or SOFA score - pre-existing chronic kidney disease
- admission to a non-ICU ward
- surgical patients
- cardiovascular disease
- emergency surgery
- on MV
CAUSE
Pre-renal
- volume responsive AKI -> monitor haemodynamics and challenge with volume
- sepsis-induced AKI
- hypotension – manage aggressively
- renovascular disorders
Renal
- nephrotoxins
— allopurinol, aminoglycosides, amphotericin, frusemide, NSAIDS, ACE-I, organic solvents, contrast, sulfondamides, thiazides, herbal medicines, heavy metals, pentamidine, paraquat - glomerular disease
- HUS
- crystal nephropathy
- tubulointerstitial disease
- rhabdomyolysis
Post-renal
- obstruction at any post-renal site (e.g. tumour, clot, papillary necrosis, foreign body, post-surgical, blocked IDC)
- abdominal compartment syndrome
Can also be categorised as:
- volume-responsive (50%)
- sepsis-induced (contributes to 50%)
- hypotension-related (Rx with fluids and noradrenaline)
- post-operative (combination of the above, with possible vascular or post-renal factors)
CONSEQUENCES OF AKI
AKI is a systemic disorder!
- Volume overload – CHF, HTN, decreased Q
- Metabolic acidosis
– hyperchloraemia
— accumulation of organic anions – PO4
— decreased Alb -> decreased buffering
— impaired insulin action -> hyperglycaemia
— catcholamine resistance (bAR downregulation)
— increased iNOS - Electrolytes – increased K+ and low Na+
- Pulmonary oedema – low albumin -> decreased oncotic pressure + volume overload
- ALI – neutrophil activation and sequestration in the lung
- Uraemia
- Immune – decreased clearance of oxidant stress, tissue oedema, WCC dysfunction – increased risk of infection
- Haematological – decreased RBC synthesis and increased destruction of RBC -> anaemia, decreased EPO, vWF -> bleeding
- GI – GI oedema -> compartment syndrome, decreased nutritional absorption, gut ischaemia -> peptic ulcer disease
- Pharmacology – increased Vd, decreased bioavailablity, albumin, decreased elimination -> under dosing or toxicity
Reasons for Dialysis/Ultrafiltration (UFAKE or AEIOU)
- Uraemic encephalopathy or uraemic pericarditis
- Fluid overload
- Acidosis
- K+
- Extras (TNT = tox, Na (hi/low), temperature)
- Acidosis
- Electrolyte abnormalities-hyperkalemia
- Ingestion of toxic substances like toxic alcohols, lithium, potassium, theophyline, barbiturates, valproate
- Overload fluid (unresponsive to diuretics)
- Uremia symptoms (pericarditis, encephalopathy)
MANAGEMENT
Specific therapy for AKI
- rule out obstructive causes and decompress (e.g. IDC, SPC, stent, nephrostomy)
- optimize preload and renal perfusion using hemodynamic monitoring +/- ino-pressors
- glomerular disease
-> confirm diagnosis
-> specific treatment with immunosuppressive drugs - interstitial nephritis (look for white cells, red cells, and white cell casts in urine sediment; eosinophiluria in 2/3)
-> treat infection (e.g.Legionella, leptospirosis, Streptococcus, CMV)
-> treat autoimmune disease
-> discontinue causative agent (e.g. antibiotics, allopurinol diuretics, PPIs, NSAIDs, indinavir, 5-aminosalicylates) - abdominal compartment syndrome
-> measure pressure (likely if IAP > 25 mmHg)
-> decompress - CRRT (intermittent haemodialysis is usually not appropriate in critically ill patients as cannot tolerate haemodynamic instability)
References and Links
Introduction to ICU Series
Introduction to ICU Series Landing Page
DAY TO DAY ICU: FASTHUG, ICU Ward Round, Clinical Examination, Communication in a Crisis, Documenting the ward round in ICU, Human Factors
AIRWAY: Bag Valve Mask Ventilation, Oropharyngeal Airway, Nasopharyngeal Airway, Endotracheal Tube (ETT), Tracheostomy Tubes
BREATHING: Positive End Expiratory Pressure (PEEP), High Flow Nasal Prongs (HFNP), Intubation and Mechanical Ventilation, Mechanical Ventilation Overview, Non-invasive Ventilation (NIV)
CIRCULATION: Arrhythmias, Atrial Fibrillation, ICU after Cardiac Surgery, Pacing Modes, ECMO, Shock
CNS: Brain Death, Delirium in the ICU, Examination of the Unconscious Patient, External-ventricular Drain (EVD), Sedation in the ICU
GASTROINTESTINAL: Enteral Nutrition vs Parenteral Nutrition, Intolerance to EN, Prokinetics, Stress Ulcer Prophylaxis (SUP), Ileus
GENITOURINARY: Acute Kidney Injury (AKI), CRRT Indications
HAEMATOLOGICAL: Anaemia, Blood Products, Massive Transfusion Protocol (MTP)
INFECTIOUS DISEASE: Antimicrobial Stewardship, Antimicrobial Quick Reference, Central Line Associated Bacterial Infection (CLABSI), Handwashing in ICU, Neutropenic Sepsis, Nosocomial Infections, Sepsis Overview
SPECIAL GROUPS IN ICU: Early Management of the Critically Ill Child, Paediatric Formulas, Paediatric Vital Signs, Pregnancy and ICU, Obesity, Elderly
FLUIDS AND ELECTROLYTES: Albumin vs 0.9% Saline, Assessing Fluid Status, Electrolyte Abnormalities, Hypertonic Saline
PHARMACOLOGY: Drug Infusion Doses, Summary of Vasopressors, Prokinetics, Steroid Conversion, GI Drug Absorption in Critical Illness
PROCEDURES: Arterial line, CVC, Intercostal Catheter (ICC), Intraosseous Needle, Underwater seal drain, Naso- and Orogastric Tubes (NGT/OGT), Rapid Infusion Catheter (RIC)
INVESTIGATIONS: ABG Interpretation, Echo in ICU, CXR in ICU, Routine daily CXR, FBC, TEG/ROTEM, US in Critical Care
ICU MONITORING: NIBP vs Arterial line, Arterial Line Pressure Transduction, Cardiac Output, Central Venous Pressure (CVP), CO2 / Capnography, Pulmonary Artery Catheter (PAC / Swan-Ganz), Pulse Oximeter
LITFL
Journal articles and Textbooks
- KDIGO Clinical Practice Guidelines for Acute Kidney Injury. Kidney International Supplements 2012;2:1
- Kellum, J. A., et al (2010) “Continuous Renal Replacement Therapy” Oxford University Press, pages 3-9 [Google Books Preview]

Critical Care
Compendium
Chris is an Intensivist and ECMO specialist at The Alfred ICU, where he is Deputy Director (Education). He is a Clinical Adjunct Associate Professor at Monash University, the Lead for the Clinician Educator Incubator programme, and a CICM First Part Examiner.
He is an internationally recognised Clinician Educator with a passion for helping clinicians learn and for improving the clinical performance of individuals and collectives. He was one of the founders of the FOAM movement (Free Open-Access Medical education) has been recognised for his contributions to education with awards from ANZICS, ANZAHPE, and ACEM.
His one great achievement is being the father of three amazing children.
On Bluesky, he is @precordialthump.bsky.social and on the site that Elon has screwed up, he is @precordialthump.
| INTENSIVE | RAGE | Resuscitology | SMACC

Great blog with very nice information! We have been looking for this type of information. Thanks a lot for sharing this kind of information. Keep posting!