Blood Products
This page is due for revision.
OVERVIEW
- important indications
- doses
- blood product compatibilities
IMPORTANT INDICATIONS
Packed red blood cells (PRBCs)
- Hb <100 and high risk of myocardial ischemia
- severe anemia (e.g. Hb<70)
- major active bleeding and Hb<100
Platelets
- <10
- <20 and high risk (fever, neutropenia, antibiotics, risk of intracranial haemorrhage)
- <50 and active bleeding or requires invasive procedure
- <80 and requires neurosurgery or ophthalmic surgery
- platelet function defects and bleeding (regardless of platelet count)
FFP
- INR >1.5 and needs invasive procedure
- INR >1.5 and actively bleeding (e.g. massive transfusion protocol, post-bypass surgery)
Cryoprecipitate
- fibrinogen <1.0 and actively bleeding (e.g. massive transfusion protocol)
- DIC
- hereditary hypofibrinogenemia, haemophilia, von Willebrand disease
Prothrombin complex concentrate (PCC)
- warfarin overdose (alternative to FFP)
Granulocyte concentrate
- neutropenic sepsis
IV immunoglobulin
- multiple — e.g. GBS, ITP, MG, vasculitis
Factor 7
- consider for rescue therapy if ongoing haemorrhage despite correction of pH and temperature, blood products to correct coagulopathy and no clear surgical cause
DOSES IN PAEDIATRICS
- Red Cells: 4ml X kg X Hb g/dL rise required. (1 unit/bag ~ 300mL)
- Fresh frozen plasma: 10 – 20 ml/kg (1 bag ~ 230mL)
- Cryoprecipitate: 5-10 ml/kg (1 bag ~ 20mL)
- Platelets: 10ml/kg (1 unit ~ 60mL. 1 pooled bag = 5 units)
- Tranexamic acid: 100mg/kg then 10mg/kg/hr
- Factor 7: 90mcg/kg
- Prothrombin (factor 9) complex: 1mL/kg (25units/kg)
BLOOD PRODUCT COMPATIBILITIES
- For RBCs: O = universal donor; AB positive = universal acceptor
- For FFP: AB = universal donor
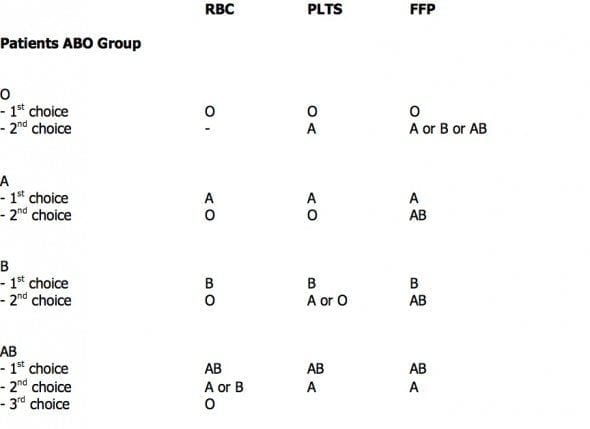
- RhD negative females of childbearing age should receive RhD negative products
- RhD negative male recipients and post-menopausal females may be transfused with RhD positive blood products with the exception of patients known to have anti-D or on regular transfusion support.

References and Links
Introduction to ICU Series
Introduction to ICU Series Landing Page
DAY TO DAY ICU: FASTHUG, ICU Ward Round, Clinical Examination, Communication in a Crisis, Documenting the ward round in ICU, Human Factors
AIRWAY: Bag Valve Mask Ventilation, Oropharyngeal Airway, Nasopharyngeal Airway, Endotracheal Tube (ETT), Tracheostomy Tubes
BREATHING: Positive End Expiratory Pressure (PEEP), High Flow Nasal Prongs (HFNP), Intubation and Mechanical Ventilation, Mechanical Ventilation Overview, Non-invasive Ventilation (NIV)
CIRCULATION: Arrhythmias, Atrial Fibrillation, ICU after Cardiac Surgery, Pacing Modes, ECMO, Shock
CNS: Brain Death, Delirium in the ICU, Examination of the Unconscious Patient, External-ventricular Drain (EVD), Sedation in the ICU
GASTROINTESTINAL: Enteral Nutrition vs Parenteral Nutrition, Intolerance to EN, Prokinetics, Stress Ulcer Prophylaxis (SUP), Ileus
GENITOURINARY: Acute Kidney Injury (AKI), CRRT Indications
HAEMATOLOGICAL: Anaemia, Blood Products, Massive Transfusion Protocol (MTP)
INFECTIOUS DISEASE: Antimicrobial Stewardship, Antimicrobial Quick Reference, Central Line Associated Bacterial Infection (CLABSI), Handwashing in ICU, Neutropenic Sepsis, Nosocomial Infections, Sepsis Overview
SPECIAL GROUPS IN ICU: Early Management of the Critically Ill Child, Paediatric Formulas, Paediatric Vital Signs, Pregnancy and ICU, Obesity, Elderly
FLUIDS AND ELECTROLYTES: Albumin vs 0.9% Saline, Assessing Fluid Status, Electrolyte Abnormalities, Hypertonic Saline
PHARMACOLOGY: Drug Infusion Doses, Summary of Vasopressors, Prokinetics, Steroid Conversion, GI Drug Absorption in Critical Illness
PROCEDURES: Arterial line, CVC, Intercostal Catheter (ICC), Intraosseous Needle, Underwater seal drain, Naso- and Orogastric Tubes (NGT/OGT), Rapid Infusion Catheter (RIC)
INVESTIGATIONS: ABG Interpretation, Echo in ICU, CXR in ICU, Routine daily CXR, FBC, TEG/ROTEM, US in Critical Care
ICU MONITORING: NIBP vs Arterial line, Arterial Line Pressure Transduction, Cardiac Output, Central Venous Pressure (CVP), CO2 / Capnography, Pulmonary Artery Catheter (PAC / Swan-Ganz), Pulse Oximeter
CCC Transfusion Series
Blood Products: Cryoprecipitate, Fresh Frozen Plasma (FFP), Platelets, Red Cells (RBCs)
>>> Factor Concentrates: Prothrombinex, Factor VIIa, Fibrinogen Concentrate
Reversal Agents:
>>> Rivaroxaban / Apixaban / Enoxaparin: Andexanet Alfa, Rivaroxaban and Bleeding
>>> Dabigatran: Idarucuzimab, Dabigatran and bleeding
>>> Heparin: Protamine
>>> Warfarin: Vitamin K, FFP, PTx, Warfarin Refersal, Warfarin Toxicity
Testing: Coagulation Studies, TEG / ROTEM (Thromboelastography), Platelet function assays
Conditions: Acute Coagulopathy of Trauma, Disseminated Intravascular Coagulation (DIC), Massive Blood Loss
General Topics: Blood Bank, Blood Conservation Strategies, Blood Product Compatibilities, Blood Transfusion Risks, Massive Transfusion Protocol (MTP), Modifications to Blood Components, Procedures and Coagulopathy, Storage Lesions, TRALI, Transfusion Literature, Transfusion Reactions
- RCH Melbourne CPG — Blood Product Transfusion

Critical Care
Compendium
Chris is an Intensivist and ECMO specialist at The Alfred ICU, where he is Deputy Director (Education). He is a Clinical Adjunct Associate Professor at Monash University, the Lead for the Clinician Educator Incubator programme, and a CICM First Part Examiner.
He is an internationally recognised Clinician Educator with a passion for helping clinicians learn and for improving the clinical performance of individuals and collectives. He was one of the founders of the FOAM movement (Free Open-Access Medical education) has been recognised for his contributions to education with awards from ANZICS, ANZAHPE, and ACEM.
His one great achievement is being the father of three amazing children.
On Bluesky, he is @precordialthump.bsky.social and on the site that Elon has screwed up, he is @precordialthump.
| INTENSIVE | RAGE | Resuscitology | SMACC
